GABAB receptors within the central nucleus of amygdala may involve in the morphine-induced incentive tolerance in female rats
- PMID: 28852448
- PMCID: PMC5569599
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.9018
GABAB receptors within the central nucleus of amygdala may involve in the morphine-induced incentive tolerance in female rats
Abstract
Objectives: Central nucleus of amygdala (CeA) is the most important region for morphine-induced reward, and GABAergic system plays an important role on morphine reinforcement. The influence of CeA administration of GABAB receptor agonist and antagonist on the expression and acquisition of morphine-induced incentive tolerance using conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm was investigated in the present study. Our purpose was to evaluate the role of CeA GABAB receptors in morphine tolerance.
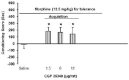
Materials and methods: Seven days after surgery and cannulation, the experiments were begun. Subcutaneous (SC) injections of morphine induced CPP. Administration of one daily dose of morphine (12.5 mg/kg) for 3 days in order to develop tolerance to the drug reduced the conditioning induced by morphine (7.5 mg/kg, SC). GABAB receptor agonist, baclofen (1.5, 6 and 12 µg/rat) or GABAB receptor antagonist, CGP35348 (1.5, 6 and 12 µg/rat) were injected into the CeA 5 min before the experiments in the test day (expression of tolerance) or 5 min before each injection of morphine (12.5 mg/kg) (acquisition of tolerance).
Results: It was shown that injections of baclofen (1.5 and 12 µg/rat) reduced acquisition, whereas the dose of 6 µg/rat of the drug exacerbated the acquisition of morphine tolerance. Baclofen at all doses significantly increased the expression of tolerance to morphine. Administration of CGP35348 (1.5, 6 and 12 µg/rat) reduced the acquisition and expression of morphine tolerance.
Conclusion: These results confirmed the importance of GABAB receptors with in the CeA in morphine tolerance in female rats.
Keywords: Central nucleus of amygdala; Conditioned place preference; GABAB receptors; Morphine; Tolerance.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Involvement of dopamine D2 receptors of the central amygdala on the acquisition and expression of morphine-induced place preference in rat.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2002 Dec;74(1):187-97. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(02)00989-9. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2002. PMID: 12376167
-
GABAB receptors within the ventral tegmental area are involved in the expression and acquisition of morphine-induced place preference in morphine-sensitized rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009 Jan;91(3):409-16. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.08.015. Epub 2008 Aug 23. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009. PMID: 18789350
-
Morphine-induced place preference: involvement of the central amygdala NMDA receptors.Brain Res. 2007 Feb 16;1133(1):34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.11.049. Epub 2006 Dec 20. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17184750
-
Intervention of the Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Type B Receptors of the Amygdala Central Nucleus on the Sensitivity of the Morphine-Induced Conditionally Preferred Location in Wistar Female Rats.Addict Health. 2017 Apr;9(2):110-117. Addict Health. 2017. PMID: 29299214 Free PMC article.
-
[Involvement of the amygdala on place aversion induced by naloxone in single-dose morphine-treated rats].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008 Mar;128(3):395-403. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.128.395. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 18311059 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Effects of Isoniazid on Tolerance and Sensitization to the Rewarding Properties of Morphine: A Conditioned Place Preference Procedure Investigation in Mice.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2020 Jul-Aug;11(4):481-490. doi: 10.32598/bcn.11.4.1940.1. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33613886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morris BJ, Herz A. Control of opiate receptor numberin vivo: Simultaneous κ-receptor down-regulation and μ-receptor up-regulation following chronic agonist/antagonist treatment. Neuroscience. 1989;29:433–442. - PubMed
-
- Khatibi A, Haghparast A, Shams J, Dianati E, Komaki A, Kamalinejad M. Effects of the fruit essential oil of Cuminum cyminum L on the acquisition and expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Neurosci lett. 2008;448:94–98. - PubMed
-
- Sahraei H, Falahi M, Zarrindast MR, Sabetkasaei M, Ghoshooni H, Khalili M. The effects of nitric oxide on the acquisition and expression of nicotine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;503:81–87. - PubMed
-
- Kiraly K, Caputi FF, Hanuska A, Kató Eb, Balogh M, Köles Ls, et al. A new potent analgesic agent with reduced liability to produce morphine tolerance. Brain Res Bull. 2015;117:32–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
