Laparoscopic splenic cyst fenestration-a viable spleen preserving option
- PMID: 28852463
- PMCID: PMC5570058
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjx154
Laparoscopic splenic cyst fenestration-a viable spleen preserving option
Abstract
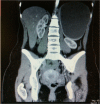
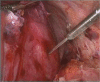
Cystic lesions of the spleen are a rare encounter in surgical practice and are broadly split into two categories: true and false, depending upon the presence of a defined epithelial lining. True cysts can further be broken down into parasitic and non-parasitic origins while false or pseudocysts tend to develop commonly after a traumatic event. We present here a 23-year-old female who came to the clinic with symptoms of abdominal fullness, early satiety and left flank pain which was diagnosed as a large splenic cyst after radiology confirmation. The patient was prepared and underwent laparoscopic splenic cyst fenestration successfully without any complications. Laparoscopic fenestration for benign uncomplicated splenic cysts is a viable alternative to splenectomy with low rates of recurrence and less patient morbidity along with the advantage of preservation of splenic function.
Figures
References
-
- Hansen MB, Moller AC. Splenic cysts. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 2004;14:316–22. - PubMed
-
- Dachman AH, Ros PR, Murari PJ. Non-parasitic splenic cysts: a report of 52 cases with radiologic-pathologic correlation. Am J Radiol 1986;187:537–42. - PubMed
-
- Robertson F, Leander P, Ekberg O. Radiology of the spleen. Eur Radiol 2001;11:80–95. - PubMed
-
- Cuervo JL. Splenic epidermoid cyst: laparoscopic partial decapsulation. Cir Pediatr 2007;20:63–7. - PubMed
-
- Trompetas V, Panagopoulos E, Priovolou-Papaevangelou M, Ramantanis G. Giant benign true cyst of the spleen with high serum level of CA 19-9. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2002;14:85–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources