Hepatic Immune Microenvironment in Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Liver Disease
- PMID: 28852648
- PMCID: PMC5567444
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/6862439
Hepatic Immune Microenvironment in Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Liver Disease
Abstract
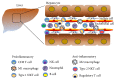
Many types of innate (natural killer cells, natural killer T cells, and Kupffer cells/macrophages) and adaptive (T cells and B cells) immune cells are enriched within the liver and function in liver physiology and pathology. Liver pathology is generally induced by two types of immunologic insults: failure to eliminate antigens derived from the gastrointestinal tract which are important for host defense and an impaired tissue protective tolerance mechanism that helps reduce the negative outcomes of immunopathology. Accumulating evidence from the last several decades suggests that hepatic immune cells play an important role in the pathogenesis of alcoholic and nonalcoholic liver injury and inflammation in humans and mice. Here, we focus on the roles of innate and adaptive immune cells in the development and maintenance of alcoholic liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Additionally, the pathogenesis of liver disease and new therapeutic targets for preventing and treating alcoholic liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis are discussed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of immune mechanisms in alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a 2015 update.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;10(2):243-53. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2016.1111758. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26634783 Review.
-
Th17 involvement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Nov 7;22(41):9096-9103. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9096. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27895397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk Between Liver Macrophages and Surrounding Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 24;11:1169. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01169. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32670278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Hepatic Innate and Innate-Like Lymphocytes in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 16;11:1500. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01500. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32765518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of immune cells in metabolism-related liver inflammation and development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016 Mar;17(1):29-39. doi: 10.1007/s11154-016-9339-2. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016. PMID: 26847547 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent insight into the role of macrophage in alcohol-associated liver disease: a mini-review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Nov 29;11:1292016. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1292016. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38094617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological Inhibition of CCR2/5 Signaling Prevents and Reverses Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage, Steatosis, and Inflammation in Mice.Hepatology. 2019 Mar;69(3):1105-1121. doi: 10.1002/hep.30249. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30179264 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Cytokines on the Progression of Liver Fibrosis in Mice Infected with Echinococcus multilocularis.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Dec 24;14:5651-5660. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S344508. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34992391 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of B Cells in Adult and Paediatric Liver Injury.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 23;12:729143. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.729143. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34630404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between IL-8 Circulating Levels and TLR2 Hepatic Expression in Women with Morbid Obesity and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 11;21(11):4189. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114189. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32545403 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

