A Nano-In-Micro System for Enhanced Stem Cell Therapy of Ischemic Diseases
- PMID: 28852702
- PMCID: PMC5571461
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.7b00213
A Nano-In-Micro System for Enhanced Stem Cell Therapy of Ischemic Diseases
Abstract
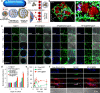
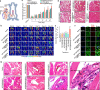
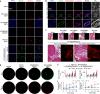
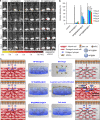
Stem cell therapy holds great potential for treating ischemic diseases. However, contemporary methods for local stem cell delivery suffer from poor cell survival/retention after injection. We developed a unique multiscale delivery system by encapsulating therapeutic agent-laden nanoparticles in alginate hydrogel microcapsules and further coentrapping the nano-in-micro capsules with stem cells in collagen hydrogel. The multiscale system exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength and stability than pure collagen hydrogel. Moreover, unlike nanoparticles, the nano-in-micro capsules do not move with surrounding body fluid and are not taken up by the cells. This allows a sustained and localized release of extracellular epidermal growth factor (EGF), a substance that could significantly enhance the proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells while maintaining their multilineage differentiation potential via binding with its receptors on the stem cell surface. As a result, the multiscale system significantly improves the stem cell survival at 8 days after implantation to ∼70% from ∼4-7% for the conventional system with nanoparticle-encapsulated EGF or free EGF in collagen hydrogel. After injecting into the ischemic limbs of mice, stem cells in the multiscale system facilitate tissue regeneration to effectively restore ∼100% blood perfusion in 4 weeks without evident side effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Luttun A.; Tjwa M.; Moons L.; Wu Y.; Angelillo-Scherrer A.; Liao F.; Nagy J. A.; Hooper A.; Priller J.; De Klerck B. Revascularization of Ischemic Tissues by Plgf Treatment, and Inhibition of Tumor Angiogenesis, Arthritis and Atherosclerosis by Anti-Flt1. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 831–840. - PubMed
-
- Zhao S.; Xu Z.; Wang H.; Reese B. F.; Gushchina L.; Jiang M.; Agarwal P.; Xu J.; Zhang M.; Shen R.; Liu Z.; Weisleder N.; He X. Bioengineering of Injectable Encapsulated Aggregates of Pluripotent Stem Cells for Therapy of Myocardial Infarction. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13306. 10.1038/ncomms13306. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

