IN VIVO AND IN VITRO IMMUNOMODULATORY AND ANTI-INFLAMMATORY EFFECTS OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS OF ASTRAGALUS
- PMID: 28852721
- PMCID: PMC5566160
- DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v13i4.10
IN VIVO AND IN VITRO IMMUNOMODULATORY AND ANTI-INFLAMMATORY EFFECTS OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS OF ASTRAGALUS
Abstract
Background: Astragali Radix has long been used to improve immune function in traditional Chinese medicine. However, its main active components and potential immunomodulatory or anti-inflammatory activities have not been elucidated. In the present study, the immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activities of total flavonoids of Astragalus (TFA) isolated from Astragali Radix were evaluated by using in vivo animal models and in vitro cell models.
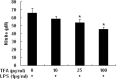
Materials and methods: The in vivo Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activities of TFA were assessed by measuring macrophage phagocytic index, delayed type hypersensitivity, serum hemolysin level and immune organ index in mice, ear edema test in mice, paw edema test in rats, vascular permeability test in mice and granuloma test in rats. The in vitro Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activities of TFA were assessed by examining its effect on cytokine and mediator production in un-stimulated and LPS-stimulated murine RAW 264.7 macrophages.
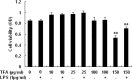
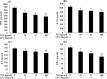
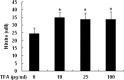
Results: The results of in vivo experiments showed that TFA enhanced macrophage phagocytic index, delayed type hypersensitivity, serum hemolysin level and immune organ index in mice, and attenuated mouse ear edema, rat paw edema, mouse vascular permeability and rat granuloma formation. The results of in vitro experiments showed that TFA stimulated the production of NO and cytokine TNF-α, IL-Ιβ, IL-6 and IFN-γ in un-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, and inhibited the overproduction of these inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages in a dose-dependent manner without exerting cytotoxicity.
Conclusion: These results of this study indicate that TFA have potential immunostimulatory and anti-inflammatory effects.
Keywords: Anti-inflammation; Immunomodulation; In vitro; In vivo; Total flavonoids of Astragalus (TFA).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective effects of total flavonoids of Astragalus against adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats by regulating OPG/RANKL/NF-κB pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Mar;44:105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.01.010. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28092862
-
Evaluation of anti-inflammatory and mechanism of action of extract of Macrosiphonia longiflora (Desf.) Müll. Arg.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Jun 11;154(2):319-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.017. Epub 2014 Mar 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24681039
-
Comparison of chemical constitution and bioactivity among different parts of Lonicera japonica Thunb.J Sci Food Agric. 2020 Jan 30;100(2):614-622. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10056. Epub 2019 Nov 14. J Sci Food Agric. 2020. PMID: 31597198
-
Advances in Chemical Composition, Extraction Techniques, Analytical Methods, and Biological Activity of Astragali Radix.Molecules. 2022 Feb 4;27(3):1058. doi: 10.3390/molecules27031058. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Composition and Therapeutic Effects of Several Astragalus Species (Fabaceae).Dokl Biol Sci. 2024 Oct;518(1):172-186. doi: 10.1134/S0012496624701096. Epub 2024 Aug 11. Dokl Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39128957 Review.
Cited by
-
Astragalus membranaceus Injection Suppresses Production of Interleukin-6 by Activating Autophagy through the AMPK-mTOR Pathway in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jul 4;2020:1364147. doi: 10.1155/2020/1364147. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32724488 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Regulation of RAW264.7 Cells In Vitro by Flavonoids from Astragalus complanatus via Activating the NF-κB Signalling Pathway.J Immunol Res. 2018 Apr 5;2018:7948068. doi: 10.1155/2018/7948068. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29850637 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Constituents Affecting the Secretion of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Induced U937 Cells by UHPLC-HRMS-Based Metabolic Profiling of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Formulation Huangqi Jianzhong Tang.Molecules. 2019 Aug 27;24(17):3116. doi: 10.3390/molecules24173116. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31461974 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Lespedeza Bicolor Extract on Regulation of AMPK Associated Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetic Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Nov 29;8(12):599. doi: 10.3390/antiox8120599. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31795363 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis and Pharmacological Activities of Flavonoids, Triterpene Saponins and Polysaccharides Derived from Astragalus membranaceus.Molecules. 2023 Jun 27;28(13):5018. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135018. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446680 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim C, Ha H, Kim J.S, Kim Y.T, Kwon S.C, Park S.W. Induction of growth hormone by the roots of Astragalus membranaceus in pituitary cell culture. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003;26:34–39. - PubMed
-
- Veterinary Pharmacopoeia Committee of PRC. Veterinary Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 2010 edition, Part 2. Chinese Agricultural Press; Beijing, China: 2011. pp. 414–416.
-
- McKenna D, Hughes K, Jones K. Astragalus Altern. Ther. Health M. 2002;8:34–40. - PubMed
-
- Cho W.C.S, Leung K.N. In vitro and in vivo immunomodulating and immunorestorative effects of Astragalus membranaceus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007;113:132–141. - PubMed
-
- Ryu M, Kim E.H, Chun M, Kang S, Shim B, Yu Y.B, Jeong G, Lee J.S. Astragali Radix elicits anti-inflammation via activation of MKP-1, concomitant with attenuation of p38 and Erk. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008;115:184–193. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
