HEXANE EXTRACT OF Dacryodes edulis FRUITS POSSESSES ANTI-DIABETIC AND HYPOLIPIDAEMIC POTENTIALS IN ALLOXAN DIABETES OF RATS
- PMID: 28852729
- PMCID: PMC5566136
- DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v13i4.18
HEXANE EXTRACT OF Dacryodes edulis FRUITS POSSESSES ANTI-DIABETIC AND HYPOLIPIDAEMIC POTENTIALS IN ALLOXAN DIABETES OF RATS
Abstract
Background: The fruit extract of Dacryodes edulis (D. edulis), the African pear or plum, a tree indigenous to the humid tropics has been used for managing wounds, skin diseases, sickle cell anaemia, dysentery and fever in some African nations. In South Eastern Nigeria, 'herbal doctors' include its marshed fruit in decoctions administered to diabetic patients. However no scientific substantiation of their claim and use exist in literature. Hence, the need to evaluate the antidiabetic and hypolipidaemic activity of hexane extracts of D. edulis fruit in alloxanised animal model.
Materials and methods: Sub-toxic doses between 400 and 1600mg/kg were orally administered sub-chronically to alloxan-induced diabetic rats for 15 days and compared to glibenclamide (2.5mg/kg). The glycaemia levels, body weights, lipid profile, blood urea, creatinine and liver enzyme levels were measured. Basic histology of the pancreatic tissue was also performed to examine the effects on the pancreas as possible mechanistic lead.
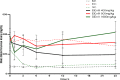
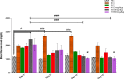
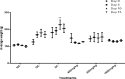
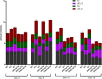
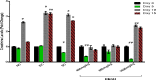
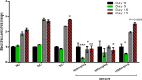
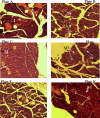
Results: Oral acute dosing of D. edulis hexane extract decreased blood glucose levels, while sub-chronic treatment of the extract down-regulated significantly hyperglycaemia, total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL-C, ALT and ALP levels. However, the HDL-C levels increased significantly. Histopathological examination of the pancreatic tissues after sub-chronic treatment showed that glibenclamide and the highest dose of the extract 1600mg/kg restored the afore-damaged pancreatic β-cell architecture.
Conclusion: Our findings portend that D. edulis hexane fruit extract possesses hypoglycaemic and hypolipidaemic activities as well as restoration of the pancreatic architecture without any obvious untoward hepatic damages, suggesting that its use in the management of the diabetes may be valid. List of Non-standard abbreviations:D. edulis = dacryode edulis, DEnH = Dacryodes edulis n-hexane fruit extract, B.wt. = Body weight, Per os = Oral administration, NC = normal control, DC =Diabetic control, SC = Standard control, LDL-C = low density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C = High density lipoprotein cholesterol, TG = Triglyceride, TC = Total cholesterol.
Keywords: Dacryodes edulis; anti-diabetic; diabetes; hypolipidaemic.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An experimental evaluation of the antidiabetic and antilipidemic properties of a standardized Momordica charantia fruit extract.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2007 Sep 24;7:29. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-7-29. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2007. PMID: 17892543 Free PMC article.
-
Possible antidiabetic and antihyperlipidaemic effect of fermented Parkia biglobosa (JACQ) extract in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006 Sep;33(9):808-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2006.04444.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16922811
-
Hypolipidaemic and antioxidant effects of fruits of Musa AAA (Chenkadali) in alloxan induced diabetic rats.Indian J Exp Biol. 2010 Feb;48(2):165-73. Indian J Exp Biol. 2010. PMID: 20455326
-
Effects of aqueous extract of alfalfa on hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia in alloxan-induced diabetic Wistar rats.Interv Med Appl Sci. 2016 Sep;8(3):103-108. doi: 10.1556/1646.8.2016.3.5. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2016. PMID: 28203391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory properties of cardiac and quercetin glycosides from Dacryodes edulis seeds during L-NAME-induced vascular perturbation.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 11;31(5):/j/jbcpp.2020.31.issue-5/jbcpp-2019-0116/jbcpp-2019-0116.xml. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2019-0116. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32653874 Review.
Cited by
-
Methanol-Extract/Fractions of Dacryodes edulis Leaves Ameliorate Hyperglycemia and Associated Oxidative Stress in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2019 Jan-Dec;24:2515690X19843832. doi: 10.1177/2515690X19843832. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 31055945 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of feed supplementation of Dacryodes edulis parts' powder as prebiotic on the growth traits, ceca microbiota and blood parameters of local chickens.Transl Anim Sci. 2020 May 21;4(2):txaa069. doi: 10.1093/tas/txaa069. eCollection 2020 Apr. Transl Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32705064 Free PMC article.
-
The Antioxidant and Antihyperglycemic Activities of Bottlebrush Plant (Callistemon lanceolatus) Stem Extracts.Medicines (Basel). 2020 Mar 4;7(3):11. doi: 10.3390/medicines7030011. Medicines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32143382 Free PMC article.
-
The Genus Dacryodes Vahl.: Ethnobotany, Phytochemistry and Biological Activities.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 22;16(5):775. doi: 10.3390/ph16050775. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicological study of aqueous-methanol solvent fraction of methanol extract of Dacryodes edulis leaves.Toxicol Rep. 2020 Jul 24;7:909-918. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.07.007. eCollection 2020. Toxicol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32775215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbate S. L, Brunzell J. D. Pathophysiology of Hyperlipidemia in Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 1990;16(Suppl 9):S1–7. - PubMed
-
- Adesokan A. A, Oyewole O. I, Turay B. M. S. Kidney and Liver Function Parameters in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats Treated with Aloe Barbadensis Juice Extract. Sierra Leone Journal of Biomedical Research. 2009;1(1):33–37.
-
- Allain C. C, Poon L. S, Chan C.S.G, Richmond W.F.P.C, Fu P. C. Enzymatic Determination of Total Serum Cholesterol. Clinical Chemistry. Am Assoc Clin Chem. 1974;20(4):470–75. - PubMed
-
- Almdal T, Henrik S, Jan S. J, Henrik V. The Independent Effect of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Ischemic Heart Disease, Stroke, and Death: A Population-Based Study of 13 000 Men and Women with 20 Years of Follow-Up. Archives of Internal Medicine. American Medical Association. 2004;164(13):1422–26. - PubMed
-
- Beagley J, Leonor G, Clara W, Ayesha A. M. Global Estimates of Undiagnosed Diabetes in Adults. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2014;103(2):150–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
