KAEMPFEROL, A FLAVONOID COMPOUND FROM GYNURA MEDICA INDUCED APOPTOSIS AND GROWTH INHIBITION IN MCF-7 BREAST CANCER CELL
- PMID: 28852738
- PMCID: PMC5566146
- DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v13i4.27
KAEMPFEROL, A FLAVONOID COMPOUND FROM GYNURA MEDICA INDUCED APOPTOSIS AND GROWTH INHIBITION IN MCF-7 BREAST CANCER CELL
Abstract
Background: Kaempferol, a natural flavonoid, has been shown to induce cancer cell apoptosis and cell growth inhibition in several tumors. Previously we have conducted a full investigation on the chemical constituents of Gynura medica, kaempferol and its glycosides are the major constituents of G. medica. Here we investigated the growth inhibition and apoptosis induction effect of kaempferol extracted from G. medica.
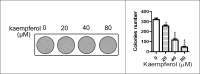
Materials and methods: The inhibition effects of kaempferol were evaluated by MTS assay and soft agar colony formation assay. Fluorescence staining and western blotting were be used to study the apoptosis. The structure was identified by 1H- NMR), 13C-NMR and ESI-MS analyses.
Results: Our results showed that kaempferol's inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth may through inducing apoptosis and downregulation of Bcl2 expression.
Conclusion: Kaempferol is a promising cancer preventive and therapeutic agent for breast cancer. List of non-standard abbreviations: MTS: 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, HPLC: High-performance liquid chromatography, NMR: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, ESI-MS Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectral, PARP: Poly ADP-ribose polymerase.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Breast Cancer; Kaempferol.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Kaempferol Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, and DNA Damage in Breast Cancer Cells.Oncol Res. 2019 Jun 21;27(6):629-634. doi: 10.3727/096504018X15228018559434. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 29739490 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrocorydaline inhibits breast cancer cells proliferation by inducing apoptosis in MCF-7 cells.Am J Chin Med. 2012;40(1):177-85. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X12500140. Am J Chin Med. 2012. PMID: 22298457
-
[Kaempferol-induced apoptosis of human esophageal squamous carcinoma Eca-109 cells and the mechanism].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011 Aug;31(8):1440-2. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21868342 Chinese.
-
[Review on experimental research of Chinese herbal medicine intervenion for breast cancer].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2007 Sep;32(18):1947-50. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18051911 Review. Chinese.
-
The Anticancer Effects and Therapeutic Potential of Kaempferol in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 23;16(15):2392. doi: 10.3390/nu16152392. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39125273 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential of Kalanchoe pinnata as a Cancer Treatment Adjuvant and an Epigenetic Regulator.Molecules. 2022 Sep 29;27(19):6425. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196425. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological Potential of Kaempferol, a Flavonoid in the Management of Pathogenesis via Modulation of Inflammation and Other Biological Activities.Molecules. 2024 Apr 26;29(9):2007. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092007. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaempferol inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of liver cancer HepG2 cells by down-regulation of microRNA-21.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2018 Mar-Dec;32:2058738418814341. doi: 10.1177/2058738418814341. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2018. Retraction in: Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021 Jan-Dec;35:20587384211040394. doi: 10.1177/20587384211040394. PMID: 30477356 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Photoaging Protective Effects of Ranunculus bulumei Methanol Extract.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Apr 3;2020:1761785. doi: 10.1155/2020/1761785. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32328122 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling Potential Health-Beneficial Properties of Corema album Phenolic Compounds: A Systematic Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 8;15(10):1231. doi: 10.3390/ph15101231. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Calderon-Montano J. M, Burgos-Moron E, Perez-Guerrero C, Lopez-Lazaro M. A review on the dietary flavonoid kaempferol. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2011;11(4):298–344. - PubMed
-
- Dang Q, Song W, Xu D, Ma Y, Li F, Zeng J, Li L. Kaempferol suppresses bladder cancer tumor growth by inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis. Mol Carcinog. 2015;54(9):831–840. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Closas R, Gonzalez C. A, Agudo A, Riboli E. Intake of specific carotenoids and flavonoids and the risk of gastric cancer in Spain. Cancer Causes Control. 1999;10(1):71–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
