Take time: odor coding capacity across sensory neurons increases over time in Drosophila
- PMID: 28852844
- PMCID: PMC5696509
- DOI: 10.1007/s00359-017-1209-1
Take time: odor coding capacity across sensory neurons increases over time in Drosophila
Abstract
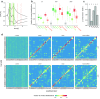
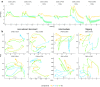
Due to the highly efficient olfactory code, olfactory sensory systems are able to reliably encode enormous numbers of olfactory stimuli. The olfactory code consists of combinatorial activation patterns across sensory neurons, thus its capacity exceeds the number of involved classes of sensory neurons by a manifold. Activation patterns are not static but vary over time, caused by the temporally complex response dynamics of the individual sensory neuron responses. We systematically analyzed the temporal dynamics of olfactory sensory neuron responses to a diverse set of odorants. We find that response dynamics depend on the combination of sensory neuron and odorant and that information about odorant identity can be extracted from the time course of the response. We also show that new response dynamics can arise when mixing two odorants. Our data show that temporal dynamics of odorant responses are able to significantly enhance the coding capacity of olfactory sensory systems.
Keywords: Adaptation; Combinatorial code; Odor mixture; Olfaction; Temporal code.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
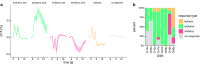
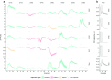
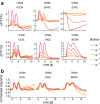
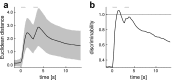
Similar articles
-
Odor-evoked inhibition of olfactory sensory neurons drives olfactory perception in Drosophila.Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 7;8(1):1357. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01185-0. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29116083 Free PMC article.
-
Learned odor discrimination in Drosophila without combinatorial odor maps in the antennal lobe.Curr Biol. 2008 Nov 11;18(21):1668-74. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.08.071. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Curr Biol. 2008. PMID: 18951022 Free PMC article.
-
Is there a space-time continuum in olfaction?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Jul;66(13):2135-50. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0011-9. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19294334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structured Odorant Response Patterns across a Complete Olfactory Receptor Neuron Population.Neuron. 2019 Mar 6;101(5):950-962.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.12.030. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 30683545 Free PMC article.
-
Odor coding in the mammalian olfactory epithelium.Cell Tissue Res. 2021 Jan;383(1):445-456. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03327-1. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Cell Tissue Res. 2021. PMID: 33409650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Olfactory Object Recognition Based on Fine-Scale Stimulus Timing in Drosophila.iScience. 2019 Mar 29;13:113-124. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.02.014. Epub 2019 Feb 18. iScience. 2019. PMID: 30826726 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory Receptor Responses to Pure Odorants in Drosophila melanogaster.Eur J Neurosci. 2025 Mar;61(5):e70036. doi: 10.1111/ejn.70036. Eur J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40062376 Free PMC article.
-
Strength in diversity: functional diversity among olfactory neurons of the same type.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2019 Feb;51(1):65-75. doi: 10.1007/s10863-018-9779-3. Epub 2019 Jan 2. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2019. PMID: 30604088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of odor sampling strategies in mice.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 14;15(8):e0237756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237756. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32797072 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium Imaging and the Curse of Negativity.Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Jan 6;14:607391. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2020.607391. eCollection 2020. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 33488363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham NM, Spors H, Carleton A, Margrie TW, Kuner T, Schaefer AT. Maintaining accuracy at the expense of speed: stimulus similarity defines odor discrimination time in mice. Neuron. 2004;44(5):865–876. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

