Comparative study of chemical neuroanatomy of the olfactory neuropil in mouse, honey bee, and human
- PMID: 28852854
- PMCID: PMC5832527
- DOI: 10.1007/s00422-017-0728-8
Comparative study of chemical neuroanatomy of the olfactory neuropil in mouse, honey bee, and human
Abstract
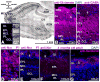
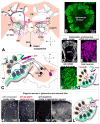
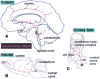
Despite divergent evolutionary origins, the organization of olfactory systems is remarkably similar across phyla. In both insects and mammals, sensory input from receptor cells is initially processed in synaptically dense regions of neuropil called glomeruli, where neural activity is shaped by local inhibition and centrifugal neuromodulation prior to being sent to higher-order brain areas by projection neurons. Here we review both similarities and several key differences in the neuroanatomy of the olfactory system in honey bees, mice, and humans, using a combination of literature review and new primary data. We have focused on the chemical identity and the innervation patterns of neuromodulatory inputs in the primary olfactory system. Our findings show that serotonergic fibers are similarly distributed across glomeruli in all three species. Octopaminergic/tyraminergic fibers in the honey bee also have a similar distribution, and possibly a similar function, to noradrenergic fibers in the mammalian OBs. However, preliminary evidence suggests that human OB may be relatively less organized than its counterparts in honey bee and mouse.
Keywords: Antennal lobe; Honey bee; Human olfaction; Noradrenaline; Octopamine; Serotonin.
Figures

References
-
- Abel R, Rybak J, Menzel R. Structure and response patterns of olfactory interneurons in the honeybee, Apis mellifera. J Comp Neurol. 2001;437:363–383. - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh R, Hassanzadeh G, Soleimani M, Joghataei Mt, Siavashi V, Khorgami Z, Hadjighassem M. Gender and age related changes in number of dopaminergic neurons in adult human olfactory bulb. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy. 2015;69:1–6. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2015.07.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baker KG, Tork I, Hornung JP, Halasz P. The human locus coeruleus complex: an immunohistochemical and three dimensional reconstruction study. Exp Brain Res. 1989;77:257–270. - PubMed
-
- Belkin K, Martin R, Kemp SE, Gilbert AN. Auditory Pitch as a Perceptual Analogue to Odor Quality. Psychological Science. 1997;8:340–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.1997.tb00450.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

