A new method to evaluate anti-allergic effect of food component by measuring leukotriene B4 from a mouse mast cell line
- PMID: 28852902
- PMCID: PMC5809648
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-017-0129-9
A new method to evaluate anti-allergic effect of food component by measuring leukotriene B4 from a mouse mast cell line
Abstract
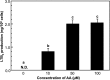
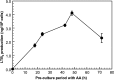
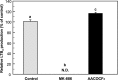
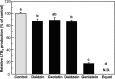
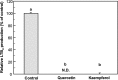
Leukotrienes (LTs), chemical mediators produced by mast cells, play an important role in allergic symptoms such as food allergies and hay fever. We tried to construct an evaluation method for the anti-LTB4 activity of chemical substances using a mast cell line, PB-3c. PB-3c pre-cultured with or without arachidonic acid (AA) was stimulated by calcium ionophore (A23187) for 20 min, and LTB4 production by the cells was determined by HPLC with UV detection. LTB4 was not detected when PB-3c was pre-cultured without AA. On the other hand, LTB4 production by PB-3c pre-cultured with AA was detectable by HPLC, and the optimal conditions of PB-3c for LTB4 detection were to utilize the cells pre-cultured with 50 µM AA for 48 h. MK-886 (5-lipoxygenase inhibitor) completely inhibited LTB4 production, but AACOCF3 (phospholipase A2 inhibitor) slightly increased LTB4 production, suggesting that LTB4 was generated from exogenous free AA through 5-lipoxygenase pathway. We applied this technique to the evaluation of the anti-LTB4 activity of food components. PB-3c pre-cultured with 50 µM AA for 48 h was stimulated with A23187 in the presence of 50 µM soybean isoflavones (daidzin, genistin, daidzein, and genistein), equol, quercetin, or kaempferol. Genistein, equol, quercetin, and kaempferol strongly inhibited LTB4 production without cytotoxicity. These results suggest that a new assay system using PB-3c is convenient to evaluate LTB4 inhibition activity by food components. This method could be utilized for elucidation of the mechanisms of LTB4 release suppression by food components such as flavonoids and the structure-activity relationship.
Keywords: Allergy; Flavonoid; Isoflavone; Leukotriene; Mast cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akiyama T, Ishida J, Nakagawa S, Ogawara H, Watanabe S, Itoh N, Shibuya M, Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:5592–5595. - PubMed
-
- Bouriche H, Miles EA, Selloum L, Calder PC. Effect of Cleome arabica leaf extract, rutin and quercetin on soybean lipoxygenase activity and on generation of inflammatory eicosanoids by human neutrophils. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005;72:195–201. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2004.10.018. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

