Major Bleeding Risk During Anticoagulation with Warfarin, Dabigatran, Apixaban, or Rivaroxaban in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 28854073
- PMCID: PMC10398327
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2017.23.9.968
Major Bleeding Risk During Anticoagulation with Warfarin, Dabigatran, Apixaban, or Rivaroxaban in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
Background: The use of non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants (NOACs) has increased steadily following marketing approval; however, their relative safety in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) patients in real-world clinical practice remains unclear.
Objective: To compare the risk of major bleeding during anticoagulation therapy between warfarin and NOACs.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study analyzed administrative claims data on new NVAF users of warfarin, dabigatran, apixaban, or rivaroxaban in routine clinical care from November 2010 to February 2015 in a commercially insured population in the United States. The primary outcome was time to first major bleeding event requiring hospitalization. Patients were followed until discontinuation or switch of anticoagulants, health plan disenrollment, death, or end of study. All patient characteristics were balanced after propensity score inverse probability of treatment (IPT) weighting. Event rates by type of anticoagulant exposure were compared using IPT-weighted Cox proportional hazards models.
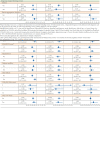
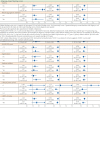
Results: The study cohort comprised 44,057 patients who used warfarin (n = 23,431), dabigatran (n = 8,539), apixaban (n = 3,689), and rivaroxaban (n = 8,398). Overall mean (SD) age was 70 (12) years, and 41% of the patients were women. A total of 2,337 major bleeding events occurred during 36,636.2 person-years of follow-up. The unadjusted rate of major bleeding with warfarin was 6.0 per 100 person-years versus 2.8 with dabigatran, 3.3 with apixban, and 5.0 with rivaroxaban. Relative to warfarin, major bleeding risk was lower with dabigatran (HR = 0.67, 95% CI = 0.60-0.76) and apixaban (HR = 0.52, 95% CI = 0.41-0.67). Compared with rivaroxaban, major bleeding risk was also lower with dabigatran (HR = 0.67, 95% CI = 0.58-0.78) and apixaban (HR = 0.52, 95% CI = 0.40-0.68). Major bleeding risk was similar for rivaroxaban and warfarin. Relative to apixaban, dabigatran was associated with a significantly higher risk of major gastrointestinal bleeding (HR = 1.43, 95% CI = 1.09-1.88).
Conclusions: Study results were consistent with safety findings from pivotal clinical trials comparing NOACs with warfarin and added the perspective of a large real-world observational study that compared bleeding risks associated with NOACs during anticoagulation therapy. Apixaban and dabigatran were associated with lower major bleeding risk compared with warfarin or rivaroxaban; however, apixaban had a lower risk of major gastrointestinal bleeding than dabigatran. These findings can help inform the choice of an optimal agent, which must balance effectiveness and bleeding risk in complex patients.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Anthem. Adeboyeje, Sylwestrzak, and Barron are employees of HealthCore, a wholly owned and independently operated subsidiary of Anthem. White, Rosenberg, Abarca, and Crawford are employees of Anthem. Study concept and design were primarily contributed by Adeboyeje and Sylwestrzak, along with the other authors. Adeboyeje took the lead in data collection, along with Sylwestrzak and Barron. Data interpretation was performed primarily by Rosenberg, Crawford, and Redberg, with assistance from the other authors. The manuscript was written by all the authors and revised primarily by White, Abarca, and Redberg, along with the other authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded by Anthem. Adeboyeje, Sylwestrzak, and Barron are employees of HealthCore, a wholly owned and independently operated subsidiary of Anthem. White, Rosenberg, Abarca, and Crawford are employees of Anthem.
Study concept and design were primarily contributed by Adeboyeje and Sylwestrzak, along with the other authors. Adeboyeje took the lead in data collection, along with Sylwestrzak and Barron. Data interpretation was performed primarily by Rosenberg, Crawford, and Redberg, with assistance from the other authors. The manuscript was written by all the authors and revised primarily by White, Abarca, and Redberg, along with the other authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral Anticoagulants for Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With High Risk of Gastrointestinal Bleeding.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Aug 2;4(8):e2120064. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.20064. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34398204 Free PMC article.
-
Bleeding risk of apixaban, dabigatran, and low-dose rivaroxaban compared with warfarin in Japanese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: a propensity matched analysis of administrative claims data.Curr Med Res Opin. 2017 Nov;33(11):1955-1963. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2017.1374935. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Curr Med Res Opin. 2017. PMID: 28857611
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Apixaban, Dabigatran, and Rivaroxaban Versus Warfarin in Patients With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation and Previous Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack.Stroke. 2017 Aug;48(8):2142-2149. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017474. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Stroke. 2017. PMID: 28655814
-
Direct comparative effectiveness and safety between non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants for stroke prevention in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.Eur J Epidemiol. 2019 Feb;34(2):173-190. doi: 10.1007/s10654-018-0415-7. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Eur J Epidemiol. 2019. PMID: 29948370
-
Real-World Use of Apixaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Stroke. 2018 Jan;49(1):98-106. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018395. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Stroke. 2018. PMID: 29167388
Cited by
-
Bleeding Risk in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Patients Receiving Direct Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies.TH Open. 2020 Jul 13;4(3):e145-e152. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1714918. eCollection 2020 Jul. TH Open. 2020. PMID: 32676543 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Anticoagulants for Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With High Risk of Gastrointestinal Bleeding.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Aug 2;4(8):e2120064. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.20064. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34398204 Free PMC article.
-
Nine-Year Trends in Prevention of Thromboembolic Complications in Elderly Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Treated with NOACs.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 21;19(19):11938. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191911938. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231248 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective cohort study of the effectiveness and safety of dabigatran versus rivaroxaban in overweight patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation.Int J Clin Pharm. 2022 Oct;44(5):1149-1157. doi: 10.1007/s11096-022-01443-2. Epub 2022 Jul 17. Int J Clin Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35842869
-
Risk Factors for Recurrent Vitreous Hemorrhage in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients after Posterior Vitrectomy.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 20;12(8):2989. doi: 10.3390/jcm12082989. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37109325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hart RG, Pearce LA, Rothbart RM, McAnulty JH, Asinger RW, Halperin JL. Stroke with intermittent atrial fibrillation: incidence and predictors during aspirin therapy. Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Investigators. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35(1):183-87. - PubMed
-
- Birman-Deych E, Radford MJ, Nilasena DS, Gage BF. Use and effectiveness of warfarin in Medicare beneficiaries with atrial fibrillation. Stroke. 2006;37(4):1070-74. - PubMed
-
- Hylek EM, Evans-Molina C, Shea C, Henault LE, Regan S. Major hemorrhage and tolerability of warfarin in the first year of therapy among elderly patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2007;115(21):2689-96. - PubMed
-
- Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, et al. . Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139-51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical