Adherence to Rivaroxaban Compared with Other Oral Anticoagulant Agents Among Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 28854075
- PMCID: PMC10397742
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2017.23.9.980
Adherence to Rivaroxaban Compared with Other Oral Anticoagulant Agents Among Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
Background: Adherence to oral anticoagulant (OAC) agents is important for patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) to prevent potentially severe adverse events.
Objective: To compare real-world adherence rates and time to discontinuation for rivaroxaban versus other OACs (apixaban, dabigatran, and warfarin) among patients with NVAF using claims-based data.
Methods: Health care claims from the IMS Health Real-World Data Adjudicated Claims database (July 2012-June 2015) were analyzed. Adherence rate was defined as the percentage of patients with proportion of days covered (PDC) ≥ 0.80 and ≥ 0.90. Discontinuation was defined as a gap of more than 30 days between the end of a dispensing days of supply and the start date of the next fill, if any. Patients were included if they had ≥ 2 dispensings of rivaroxaban, apixaban, dabigatran, or warfarin at least 180 days apart (the first was considered the index date), had > 60 days of supply, had ≥ 6 months of pre-index eligibility, had ≥ 1 atrial fibrillation (AF) diagnosis pre-index or at index date, and had no valvular involvement. A logistic regression model was used to evaluate adherence to OAC therapy, while a Cox model was used to compare time to discontinuation; both models adjusted for baseline confounders.
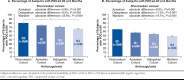
Results: A total of 13,645 rivaroxaban, 6,304 apixaban, 3,360 dabigatran, and 13,366 warfarin patients were identified. A significantly higher proportion of rivaroxaban users (80.1%) was adherent to therapy (PDC ≥ 0.80 at 6 months) versus apixaban (75.8%), dabigatran (69.2%), and warfarin users (64.5%). After adjustment, the proportion of patients adherent to therapy remained significantly higher for rivaroxaban users versus apixaban (absolute difference [AD] = 5.8%), dabigatran (AD = 9.5%), and warfarin users (AD = 13.6%; all P < 0.001). More pronounced differences were found with a PDC ≥0.90. In addition, rivaroxaban users were significantly less likely to discontinue therapy compared with other OACs after adjustments (all P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Among NVAF patients, rivaroxaban was associated with significantly higher adherence rates relative to other OACs whether using either a PDC of > 0.80 or > 0.90. Such differences in adherence could translate into improved patient outcomes and lower health care costs.
Disclosures: This research was funded by Janssen Scientific Affairs. Ashton, Crivera, and Schein are employees and stockholders of Janssen Scientific Affairs. Laliberté, Germain, Wynant, and Lefebvre are employees of Analysis Group, a consulting company that received research grants from Janssen Scientific Affairs in connection with this study. McHorney is an employee of Evidera, a consulting company that received research grants from Janssen Scientific Affairs in connection with this study. Peterson received research grants from Janssen Scientific Affairs in connection with this study. All authors contributed to concept and design. The data were collected by Germain, Wynant, Laliberté, and Lefebvre and interpreted primarily by McHorney and Peterson, with the assistance of Lefebvre, Laliberté, Ashton, Crivera, and Schein. The manuscript was written primarily by Laliberté, Germain, and Lefebvre, with the assistance of Wynant. Revisions were made primarily by Ashton, Crivera, McHorney, Schein, and Peterson.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was funded by Janssen Scientific Affairs. Ashton, Crivera, and Schein are employees and stockholders of Janssen Scientific Affairs. Laliberté, Germain, Wynant, and Lefebvre are employees of Analysis Group, a consulting company that received research grants from Janssen Scientific Affairs in connection with this study. McHorney is an employee of Evidera, a consulting company that received research grants from Janssen Scientific Affairs in connection with this study. Peterson received research grants from Janssen Scientific Affairs in connection with this study.
All authors contributed to concept and design. The data were collected by Germain, Wynant, Laliberté, and Lefebvre and interpreted primarily by McHorney and Peterson, with the assistance of Lefebvre, Laliberté, Ashton, Crivera, and Schein. The manuscript was written primarily by Laliberté, Germain, and Lefebvre, with the assistance of Wynant. Revisions were made primarily by Ashton, Crivera, McHorney, Schein, and Peterson.
Figures
References
-
- Colilla S, Crow A, Petkun W, et al. Estimates of current and future incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation in the U.S. adult population. Am J Cardiol. 2013;112(8):1142-47. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, et al. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA. 2001;285(18):2370. - PubMed
-
- Coyne KS, Paramore C, Grandy S, et al. Assessing the direct costs of treating nonvalvular atrial fibrillation in the United States. Value Health. 2006;9(5):348-56. - PubMed
-
- Spencer RJ, Amerena J V. Rivaroxaban in the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: clinical implications of the ROCKET AF Trial and its subanalyses. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2015;15(6):395-401. - PubMed
-
- Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991;22(8):983-88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous