Automated diagnosis of myositis from muscle ultrasound: Exploring the use of machine learning and deep learning methods
- PMID: 28854220
- PMCID: PMC5576677
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184059
Automated diagnosis of myositis from muscle ultrasound: Exploring the use of machine learning and deep learning methods
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the use of ultrasound coupled with machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) techniques for automated or semi-automated classification of myositis.
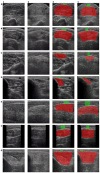
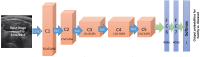
Methods: Eighty subjects comprised of 19 with inclusion body myositis (IBM), 14 with polymyositis (PM), 14 with dermatomyositis (DM), and 33 normal (N) subjects were included in this study, where 3214 muscle ultrasound images of 7 muscles (observed bilaterally) were acquired. We considered three problems of classification including (A) normal vs. affected (DM, PM, IBM); (B) normal vs. IBM patients; and (C) IBM vs. other types of myositis (DM or PM). We studied the use of an automated DL method using deep convolutional neural networks (DL-DCNNs) for diagnostic classification and compared it with a semi-automated conventional ML method based on random forests (ML-RF) and "engineered" features. We used the known clinical diagnosis as the gold standard for evaluating performance of muscle classification.
Results: The performance of the DL-DCNN method resulted in accuracies ± standard deviation of 76.2% ± 3.1% for problem (A), 86.6% ± 2.4% for (B) and 74.8% ± 3.9% for (C), while the ML-RF method led to accuracies of 72.3% ± 3.3% for problem (A), 84.3% ± 2.3% for (B) and 68.9% ± 2.5% for (C).
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the application of machine learning methods for automatically or semi-automatically classifying inflammatory muscle disease using muscle ultrasound. Compared to the conventional random forest machine learning method used here, which has the drawback of requiring manual delineation of muscle/fat boundaries, DCNN-based classification by and large improved the accuracies in all classification problems while providing a fully automated approach to classification.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Pillen S, Boon A, Van Alfen N. Muscle ultrasound In: Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Volume 136; 2016. p. 843–853. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

