Sulforaphane suppresses PRMT5/MEP50 function in epidermal squamous cell carcinoma leading to reduced tumor formation
- PMID: 28854561
- PMCID: PMC5862259
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgx044
Sulforaphane suppresses PRMT5/MEP50 function in epidermal squamous cell carcinoma leading to reduced tumor formation
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Sulforaphane suppresses PRMT5/MEP50 function in epidermal squamous cell carcinoma leading to reduced tumor formation.Carcinogenesis. 2023 Oct 20;44(7):626-627. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgad044. Carcinogenesis. 2023. PMID: 37549132 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
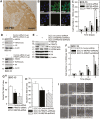
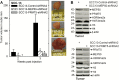
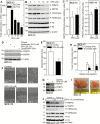
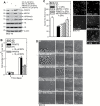
Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) cooperates with methylosome protein 50 (MEP50) to arginine methylate histone H3 and H4 to silence gene expression, and increased PRMT5 activity is associated with enhanced cancer cell survival. We have studied the role of PRMT5 and MEP50 in epidermal squamous cell carcinoma. We show that knockdown of PRMT5 or MEP50 results in reduced H4R3me2s formation, and reduced cell proliferation, invasion, migration and tumor formation. We further show that treatment with sulforaphane (SFN), a cancer preventive agent derived from cruciferous vegetables, reduces PRMT5 and MEP50 level and H4R3me2s formation, and this is associated with reduced cell proliferation, invasion and migration. The SFN-dependent reduction in PRMT5 and MEP50 level requires proteasome activity. Moreover, SFN-mediated responses are partially reversed by forced PRMT5 or MEP50 expression. SFN treatment of tumors results in reduced MEP50 level and H4R3me2s formation, confirming that that SFN impacts this complex in vivo. These studies suggest that the PRMT5/MEP50 is required for tumor growth and that reduced expression of this complex is a part of the mechanism of SFN suppression of tumor formation.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2024 Aug 15;89(158):66420-66422. Fed Regist. 2024. PMID: 39161428 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tanaka, H., et al. (2009) PRMT5, a novel TRAIL receptor-binding protein, inhibits TRAIL-induced apoptosis via nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Mol. Cancer Res., 7, 557–569. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

