Bio-Docklets: virtualization containers for single-step execution of NGS pipelines
- PMID: 28854616
- PMCID: PMC5569920
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/gix048
Bio-Docklets: virtualization containers for single-step execution of NGS pipelines
Abstract
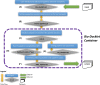
Processing of next-generation sequencing (NGS) data requires significant technical skills, involving installation, configuration, and execution of bioinformatics data pipelines, in addition to specialized postanalysis visualization and data mining software. In order to address some of these challenges, developers have leveraged virtualization containers toward seamless deployment of preconfigured bioinformatics software and pipelines on any computational platform. We present an approach for abstracting the complex data operations of multistep, bioinformatics pipelines for NGS data analysis. As examples, we have deployed 2 pipelines for RNA sequencing and chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, preconfigured within Docker virtualization containers we call Bio-Docklets. Each Bio-Docklet exposes a single data input and output endpoint and from a user perspective, running the pipelines as simply as running a single bioinformatics tool. This is achieved using a "meta-script" that automatically starts the Bio-Docklets and controls the pipeline execution through the BioBlend software library and the Galaxy Application Programming Interface. The pipeline output is postprocessed by integration with the Visual Omics Explorer framework, providing interactive data visualizations that users can access through a web browser. Our goal is to enable easy access to NGS data analysis pipelines for nonbioinformatics experts on any computing environment, whether a laboratory workstation, university computer cluster, or a cloud service provider. Beyond end users, the Bio-Docklets also enables developers to programmatically deploy and run a large number of pipeline instances for concurrent analysis of multiple datasets.
Keywords: CHIPseq; NGS; RNAseq; bioinformatics; docker.
© The Authors 2017. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miCloud: A Plug-n-Play, Extensible, On-Premises Bioinformatics Cloud for Seamless Execution of Complex Next-Generation Sequencing Data Analysis Pipelines.J Comput Biol. 2019 Mar;26(3):280-284. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2018.0218. Epub 2019 Jan 17. J Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 30653336 Free PMC article.
-
DolphinNext: a distributed data processing platform for high throughput genomics.BMC Genomics. 2020 Apr 19;21(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6714-x. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32306927 Free PMC article.
-
Closha 2.0: a bio-workflow design system for massive genome data analysis on high performance cluster infrastructure.BMC Bioinformatics. 2024 Nov 12;25(1):353. doi: 10.1186/s12859-024-05963-8. BMC Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 39533201 Free PMC article.
-
Containers in Bioinformatics: Applications, Practical Considerations, and Best Practices in Molecular Pathology.J Mol Diagn. 2022 May;24(5):442-454. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2022.01.006. Epub 2022 Feb 18. J Mol Diagn. 2022. PMID: 35189355 Review.
-
Using R and Bioconductor in Clinical Genomics and Transcriptomics.J Mol Diagn. 2020 Jan;22(1):3-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2019.08.006. Epub 2019 Oct 9. J Mol Diagn. 2020. PMID: 31605800 Review.
Cited by
-
Democratizing bioinformatics through easily accessible software platforms for non-experts in the field.Biotechniques. 2022 Feb;72(2):36-38. doi: 10.2144/btn-2021-0060. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Biotechniques. 2022. PMID: 35060754 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
YAMP: a containerized workflow enabling reproducibility in metagenomics research.Gigascience. 2018 Jul 1;7(7):giy072. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giy072. Gigascience. 2018. PMID: 29917068 Free PMC article.
-
miCloud: A Plug-n-Play, Extensible, On-Premises Bioinformatics Cloud for Seamless Execution of Complex Next-Generation Sequencing Data Analysis Pipelines.J Comput Biol. 2019 Mar;26(3):280-284. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2018.0218. Epub 2019 Jan 17. J Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 30653336 Free PMC article.
-
Towards reproducible computational drug discovery.J Cheminform. 2020 Jan 28;12(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13321-020-0408-x. J Cheminform. 2020. PMID: 33430992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harmonizing and integrating the NCI Genomic Data Commons through accessible, interactive, and cloud-enabled workflows.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 4;20(3):e0318676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318676. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40036210 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

