Extramedullary Tibial Bone Cutting Using Medial Cortical Line in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- PMID: 28854764
- PMCID: PMC5596395
- DOI: 10.5792/ksrr.16.023
Extramedullary Tibial Bone Cutting Using Medial Cortical Line in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to identify the effectiveness of the medial cortical line for attaining a more accurate tibial component alignment in proximal tibial resection using an extramedullary alignment rod.
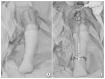
Materials and methods: The study examined 100 cases of total knee arthroplasty performed from December 2013 to February 2014 in a retrospective manner. On a preoperative anteroposterior (AP) radiograph of the entire tibia, we identified the medial cortical line that runs parallel to the tibial anatomical axis and passes the medial tibial spine, and measured the point where the medial cortical line crosses between the medial malleolus and the lateral malleolus in the ankle joint.
Results: The preoperative AP radiograph of the tibia showed the medial cortical line passing the point 40.4%±0.8% medial to the distance from the medial malleolus to the lateral malleolus including the skin thickness in the ankle joint. When the proximal tibial resection was performed with the extramedullary tibial cutting guide aligned with the medial cortical line, the tibial component angle averaged 0.7°±0.3° varus and the alignment accuracy of the tibial component within 0°±3° varus amounted to 97.0%.
Conclusions: The use of the medial cortical line in proximal tibial resection with an extramedullary tibial cutting guide allowed for relatively accurate alignment of the tibial component.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Knee; Tibial bone resection.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of ankle rotation on cutting of the tibia in total knee arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006 Dec;88(12):2632-6. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.E.01288. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. PMID: 17142413
-
Effects of tibial torsion on distal alignment of extramedullary instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty.Acta Orthop. 2013 Jun;84(3):275-9. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2013.792032. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Acta Orthop. 2013. PMID: 23594222 Free PMC article.
-
Do varus or valgus outliers have higher forces in the medial or lateral compartments than those which are in-range after a kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty? limb and joint line alignment after kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty.Bone Joint J. 2017 Oct;99-B(10):1319-1328. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.99B10.BJJ-2017-0066.R1. Bone Joint J. 2017. PMID: 28963153
-
A proposed new rotating reference axis for the tibial component after proximal tibial resection in total knee arthroplasty.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 20;13(12):e0209317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209317. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30571784 Free PMC article.
-
A sagittal reference line using the preoperative radiograph in total knee arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020 Jan-Apr;28(2):2309499020924143. doi: 10.1177/2309499020924143. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020. PMID: 32468963
References
-
- Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB. Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement. Its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(299):153–6. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda S, Miura H, Nagamine R, Urabe K, Hirata G, Iwamoto Y. Effect of femoral and tibial component position on patellar tracking following total knee arthroplasty: 10-year follow-up of Miller-Galante I knees. Am J Knee Surg. 2001;14:152–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
