Humanization of pediatric care in the world: focus and review of existing models and measurement tools
- PMID: 28854953
- PMCID: PMC5577665
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-017-0394-4
Humanization of pediatric care in the world: focus and review of existing models and measurement tools
Abstract
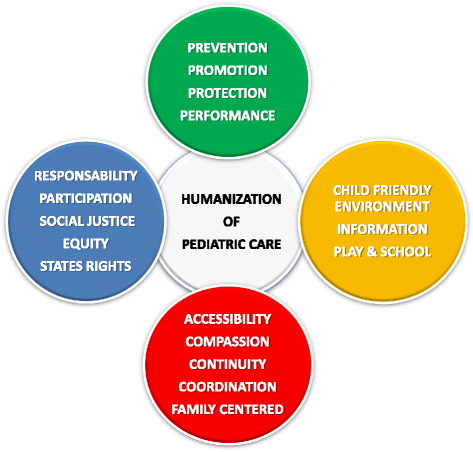
Background: The term "humanization" indicates the process by which people try to make something more human and civilized, more in line with what is believed to be the human nature. The humanization of care is an important and not yet a well-defined issue which includes a wide range of aspects related to the approach to the patient and care modalities. In pediatrics, the humanization concept is even vaguer due to the dual involvement of both the child and his/her family and by the existence of multiple proposed models.
Objective: The present study aims to analyze the main existing humanization models regarding pediatric care, and the tools for assessing its grade.
Results: The main Humanization care programs have been elaborated and developed both in America (Brazil, USA) and Europe. The North American and European models specifically concern pediatric care, while the model developed in Brazil is part of a broader program aimed at all age groups. The first emphasis is on the importance of the family in child care, the second emphasis is on the child's right to be a leader, to be heard and to be able to express its opinion on the program's own care. Several tools have been created and used to evaluate humanization of care programs and related aspects. None, however, had been mutually compared.
Conclusions: The major models of humanization care and the related assessment tools here reviewed highlight the urgent need for a more unifying approach, which may help in realizing health care programs closer to the young patient's and his/her family needs.
Keywords: Child-friendly healthcare; Family centered care; Humanization; Pediatric care.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Gargantini G. Humanization in the management of hospitalized children and adolescents. Ital J Pediatr. 2014;40(Suppl 1):A31. doi: 10.1186/1824-7288-40-S1-A31. - DOI
-
- Pasche DF. National Humanization Policy as a bet for collective production of changes in management and care methods. Interface - Comunicação Saúde Educação. 2009;13(Suppl. 1):701–708. doi: 10.1590/S1414-32832009000500021. - DOI
-
- Rede Humaniza SUS. http://www.redehumanizasus.net/4-a-rede-humaniza-sus. Accessed 23 Aug 2017.
-
- Negri B. O processo de humanização dos serviços de saúde: a experiência do Programa Nacional de Humanização da Assistência Hospitalar. http://www.saude.sc.gov.br/Eventos/Humaniza_SUS/Manual_%20Politica_Human.... Accessed 23 Aug 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

