Ultra-low dose of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 28854956
- PMCID: PMC5577818
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-2134-x
Ultra-low dose of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: A standard low-dosing schedule of rituximab (RTX; 2 × 500 mg or 1 × 1000 mg) is as effective for active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) as the registered dose (2 × 1000 mg). Moreover, several small uncontrolled studies suggest that even lower-dosed treatment with RTX also leads to good treatment response in patients with RA. Retreatment with such an 'ultra-low' dose RTX in patients who responded well to RTX induction treatment is of special interest, as long-term use of lower RTX doses may lead to shorter infusion duration, lower risk of adverse events and lower costs. However, the effect of ultra-low dose of RTX has not been investigated using a controlled trial of proper design and dimensions.
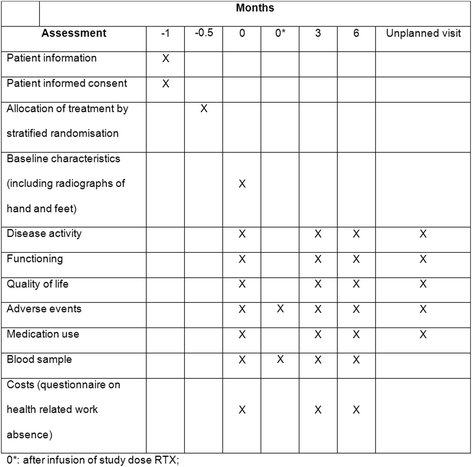
Methods/design: REDO is an investigator driven six-month pragmatic, double-blind, randomised controlled non-inferiority trial on the effects of ultra-low-dose RTX (1 × 500 or 1 × 200 mg) compared to standard low dose (1 × 1000 mg) in RA patients who are being retreated with RTX. A total of 140 RA patients, having reached low disease activity (DAS28CRP < 2.9) after the previous RTX infusion and DAS28CRP < 3.5 at moment of retreatment, are randomised in a ratio of 1:2:2 to 1 × 1000 mg, 1 × 500 mg or 1 × 200 mg. The primary objective is testing non-inferiority of the ultra-low-dose vs. standard low-dose RTX, by comparing mean change in DAS28CRP from baseline to six months to the non-inferiority margin of 0.6. Secondary outcomes over the same period are: function; quality of life; safety; costs; and pharmacokinetics and dynamics as process measures.
Discussion: This study protocol shares characteristics of both early dose finding trials as well as late pragmatic clinical studies. Several choices in the design of this trial are described and possible consequences for RA treatment and expected biosimilar introduction are discussed.
Trial registration: Dutch Trial Register, NTR6117 . Registered on 15 November 2016 (CMO NL57520.091.16 , 8 November 2016).
Keywords: Decremental cost-effectiveness ratio (DCER); Design; Dose reduction; Low dose; Non-inferiority; Randomised controlled trial; Retreatment; Rheumatoid arthritis; Rituximab.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Dutch Trial Register, NTR 6117, date 15 November 2016. The study has received ethical review board approval (number NL57520.091.16), dated 8 November 2016.
Ethics approval was obtained for all participating centres from the central Commissie Mensgebonden Onderzoek (committee of human research) CMO regio Arnhem Nijmegen, Radboud University Medical Center, PO Box 9101, 6500 HB, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. Patient informed consent will be obtained from all participants in the study.
Consent to participate
The protocol as outlined here was approved by the central medical ethical committee for all participating centres (CMO Arnhem-Nijmegen, NL57520.091.16) in 2016. The Trial is registered at NTR6117.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
Alfons A den Broeder: congress invitations with Roche, Abbvie, Biogen, Celltrion, expert witness for Amgen and BI. Rogier Thurlings: translational RTX research sponsored by Roche, congress invitations from Abbvie, Roche. Bart JF van den Bemt: Speakerfee from Abbvie, Pfizer, Mundipharma, Astra, MSD. Research grant from Pfizer, Abbvie. Frank HJ van den Hoogen: advisory board member mundipharma on RTX biosimilar, congress invitation Cellgene, international advisory board Biogen etanercept biosimilar, speakers fee biosimilars Celltrion and Egis and Janssen. The other authors declare having no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Malottki K, Barton P, Tsourapas A, Uthman AO, Liu Z, Routh K, et al. Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure of a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2011;15(14):1–278. doi: 10.3310/hta15140. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Vollenhoven RF, Emery P, Bingham CO, III, Keystone EC, Fleischmann RM, Furst DE, et al. Long-term safety of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: 9.5-year follow-up of the global clinical trial programme with a focus on adverse events of interest in RA patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(9):1496–502. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201956. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical