Evaluation of Rumex hastatus leaves against hepatic fibrosis: a rat model
- PMID: 28854968
- PMCID: PMC5577788
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1943-5
Evaluation of Rumex hastatus leaves against hepatic fibrosis: a rat model
Abstract
Background: Rumex hastatus leaves have been widely used as food additive and for the treatment of various liver ailments. According to our previous studies, ethyle acetate (ERL) and methanolic (MRL) fractions of R. hastatus leaves are an accessible source of natural antioxidants. In the present research work we arranged to investigate the R. hastatus leaves as hepaptoprotective agent verse hepatic damages caused by CCl4.
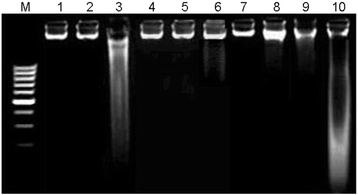
Methods: During this project we divided 48 rats into eight groups randomly. CCl4-induced damages were assessed through liver function markers viz.; alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), γ-glutamyltransferase (γ-GT) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Changes in lipid profile were checked by measuring serum total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (Tg), high density lipoproteins (HDL) and low density lipoproteins (LDL). Antioxidant status was checked by the activities of antioxidant enzymes, DNA damages and cellular abnormalities at histo level.
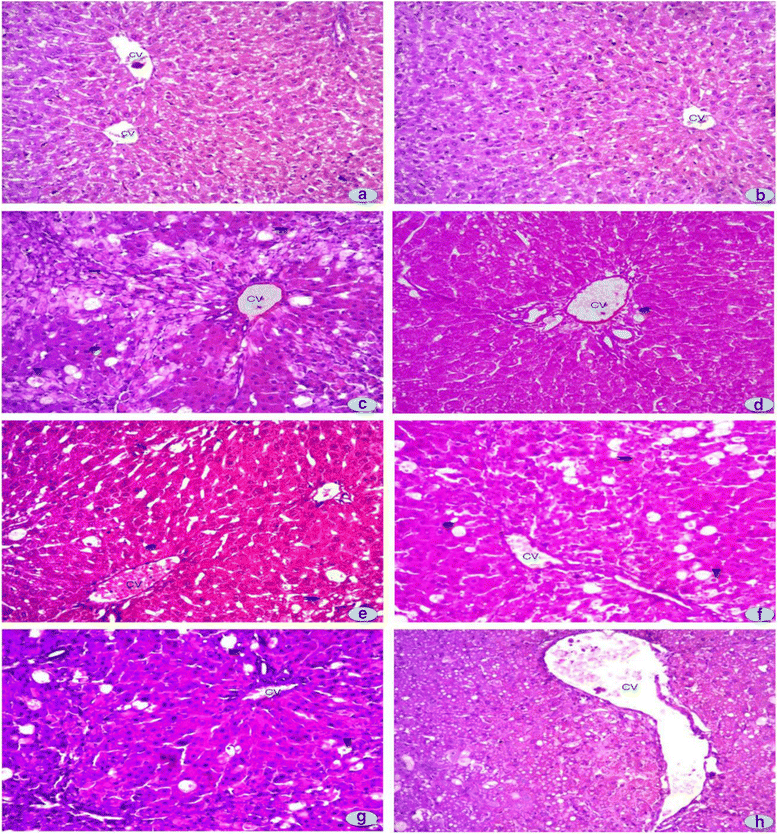
Results: Administration of CCl4 in rats caused significant increase in liver function and lipid profile indicating hepatic damages which were restored by co-administration of R. hastatus extracts. Cellular and DNA damages in hepatic tissues were caused by CCl4 which shown clear hepatic fibrosis in addition to disturb antioxidant enzyme level. Co-treatment with various fractions of R. hastatus leaves regulated these markers of oxidative dysfunctions.
Conclusion: From the present report it was inferred that R. hastatus leaves have the ability to reverse CCl4 - induced hepatic damages.
Keywords: Carbon tetrachloride; Fibrosis; Hepatotoxicity; Oxidative stress; Rumex hastatus; leaves.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was conducted according to the protocol approved by ethical committee of the University.
Consent for publication
All the authors are agreeing to submit the paper in your esteemed Journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

