Wolbachia, bottled water, and the dark side of symbiosis
- PMID: 28855327
- PMCID: PMC5576898
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E17-02-0132
Wolbachia, bottled water, and the dark side of symbiosis
Abstract
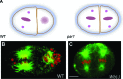
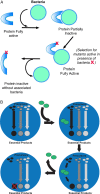
Obligate endosymbiosis is operationally defined when loss or removal of the endosymbiont from the host results in the death of both. Whereas these relationships are typically viewed as mutualistic, molecular and cellular analysis reveals numerous instances in which these symbiotic relationships are established by alternative, nonmutualistic strategies. The endosymbiont usurps or integrates into core host processes, creating a need where none previously existed. Here I discuss examples of these addictive symbiotic relationships and how they are a likely outcome of all complex evolving systems.
© 2017 Sullivan. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parasitic inhibition of cell death facilitates symbiosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 2;104(1):213-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607845104. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17190825 Free PMC article.
-
Infection density of Wolbachia endosymbiont affected by co-infection and host genotype.Biol Lett. 2005 Dec 22;1(4):488-91. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2005.0340. Biol Lett. 2005. PMID: 17148240 Free PMC article.
-
Gene conversion maintains nonfunctional transposable elements in an obligate mutualistic endosymbiont.Mol Biol Evol. 2009 Aug;26(8):1679-82. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msp093. Epub 2009 May 4. Mol Biol Evol. 2009. PMID: 19414524
-
GroEL and the maintenance of bacterial endosymbiosis.Trends Genet. 2004 Sep;20(9):413-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2004.07.001. Trends Genet. 2004. PMID: 15313549 Review.
-
The symbiotic role of Wolbachia in Onchocercidae and its impact on filariasis.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013 Feb;19(2):131-40. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12069. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013. PMID: 23398406 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of manipulative microbial behaviors in the rhizosphere.Evol Appl. 2022 Jan 14;15(10):1521-1536. doi: 10.1111/eva.13333. eCollection 2022 Oct. Evol Appl. 2022. PMID: 36330300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wolbachia: endosymbiont of onchocercid nematodes and their vectors.Parasit Vectors. 2021 May 7;14(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04742-1. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 33962669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro maintenance of the endosymbiont Wolbachia of Dirofilaria immitis.Parasitol Res. 2023 Apr;122(4):939-943. doi: 10.1007/s00436-023-07789-4. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Parasitol Res. 2023. PMID: 36810669
-
Multiple origins of obligate nematode and insect symbionts by a clade of bacteria closely related to plant pathogens.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Dec 15;117(50):31979-31986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2000860117. Epub 2020 Nov 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33257562 Free PMC article.
-
Describing endosymbiont-host interactions within the parasitism-mutualism continuum.Ecol Evol. 2024 Jul 4;14(7):e11705. doi: 10.1002/ece3.11705. eCollection 2024 Jul. Ecol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38975267 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

