β2-Adrenergic Receptor-Mediated HIF-1α Upregulation Mediates Blood Brain Barrier Damage in Acute Cerebral Ischemia
- PMID: 28855859
- PMCID: PMC5558520
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00257
β2-Adrenergic Receptor-Mediated HIF-1α Upregulation Mediates Blood Brain Barrier Damage in Acute Cerebral Ischemia
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: β2-Adrenergic Receptor-Mediated HIF-1α Upregulation Mediates Blood Brain Barrier Damage in Acute Cerebral Ischemia.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Nov 20;10:392. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00392. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29204110 Free PMC article.
Abstract
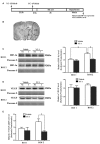
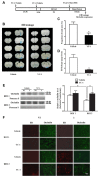
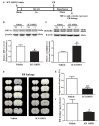
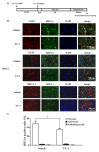
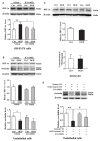
Disruption of the blood brain barrier (BBB) within the thrombolytic time window is an antecedent event to intracerebral hemorrhage in ischemic stroke. Our recent studies showed that 2-h cerebral ischemia induced BBB damage in non-infarcted area and secreted matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) accounted for this disruption. However, the factors that affect MMP-2 secretion and regulate BBB damage remains unknown. Since hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) was discovered as a mater regulator in hypoxia, we sought to investigate the roles of HIF-1α in BBB damage as well as the factors regulating HIF-1α expression in the ischemic brain. in vivo rat middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and in vitro oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD) models were used to mimic ischemia. Pretreatment with HIF-1α inhibitor YC-1 significantly inhibited 2-h MCAO-induced BBB damage, which was accompanied by suppressed occludin degradation and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA upregulation. Interestingly, β2-adrenergic receptor (β2-AR) antagonist ICI 118551 attenuated ischemia-induced BBB damage by regulating HIF-1α expression. Double immunostaining showed that HIF-1α was upregulated in ischemic neurons but not in astrocytes andendothelial cells. Of note, HIF-1α inhibition with inhibitor YC-1 or siRNA significantly prevented OGD-induced VEGF upregulation as well as the secretion of VEGF and MMP-2 in neurons. More importantly, blocking β2-AR with ICI 118551 suppressedHIF-1α upregulation in ischemic neurons and attenuated occludin degradation induced by the conditioned media of OGD-treatedneurons. Taken together, blockade of β2-AR-mediated HIF-1α upregulation mediates BBB damage during acute cerebral ischemia. These findings provide new mechanistic understanding of early BBB damage in ischemic stroke and may help reduce thrombolysis-related hemorrhagic complications.
Keywords: HIF-1α; blood brain barrier; cerebral ischemia; matrix metalloproteinase; tight junction proteins; β2-AR.
Figures


References
-
- Benchenane K., Berezowski V., Fernández-Monreal M., Brillault J., Valable S., Dehouck M. P., et al. . (2005). Oxygen glucose deprivation switches the transport of tPA across the blood-brain barrier from an LRP-dependent to an increased LRP-independent process. Stroke 36, 1065–1070. 10.1161/01.STR.0000163050.39122.4f - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bernaudin M., Nedelec A. S., Divoux D., MacKenzie E. T., Petit E., Schumann-Bard P. (2002). Normobaric hypoxia induces tolerance to focal permanent cerebral ischemia in association with an increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and its target genes, erythropoietin and VEGF, in the adult mouse brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 22, 393–403. 10.1097/00004647-200204000-00003 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

