Respiratory syncytial virus infection influences tight junction integrity
- PMID: 28856667
- PMCID: PMC5680068
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13042
Respiratory syncytial virus infection influences tight junction integrity
Abstract
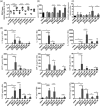
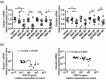
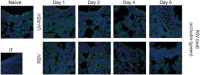
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is an important risk factor of asthma development and is responsible for severe respiratory tract infections. However, the influence of RSV infection on barrier function of bronchial epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo is still unclear. The aim of this study was to analyse the role of RSV in tight junction (TJ) regulation and to compare epithelial integrity between asthmatic and healthy individuals upon RSV infection. Healthy and asthmatic human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) were differentiated at air-liquid interface (ALI) and infected with RSV and ultraviolet (UV)-irradiated RSV. TJ expression and their integrity were analysed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), transepithelial resistance (TER) and paracellular flux. To determine the effect in vivo, BALB/c mice were infected intranasally with RSV or UV-irradiated RSV A2. Bronchoalveolar lavage and TJ integrity were analysed on days 1, 2, 4 and 6 post-infection by qPCR, bioplex and confocal microscopy. RSV increased barrier integrity in ALI cultures of HBEC from healthy subjects, but no effect was found in HBECs from asthmatics. This was not associated with an increase in TJ mRNA expression. In vivo, RSV induced lung inflammation in mice and down-regulated claudin-1 and occludin mRNA expression in whole lungs. Surprisingly, RSV infection was not observed in bronchial epithelial cells, but was found in the lung parenchyma. Decreased expression of occludin upon RSV infection was visible in mouse bronchial epithelial cells in confocal microscopy. However, there was no regulation of claudin-1 and claudin-7 at protein level.
Keywords: airway epithelial cells; asthma; respiratory syncytial virus; tight junctions.
© 2017 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

References
-
- Johnson JE, Gonzales RA, Olson SJ, Wright PF, Graham BS. The histopathology of fatal untreated human respiratory syncytial virus infection. Mod Pathol 2007; 20:108–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

