Selective synaptic connections in the retinal pathway for night vision
- PMID: 28856684
- PMCID: PMC5832573
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.24313
Selective synaptic connections in the retinal pathway for night vision
Abstract
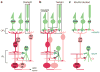
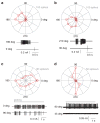
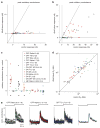
The mammalian retina encodes visual information in dim light using rod photoreceptors and a specialized circuit: rods→rod bipolar cells→AII amacrine cell. The AII amacrine cell uses sign-conserving electrical synapses to modulate ON cone bipolar cell terminals and sign-inverting chemical (glycinergic) synapses to modulate OFF cone cell bipolar terminals; these ON and OFF cone bipolar terminals then drive the output neurons, retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), following light increments and decrements, respectively. The AII amacrine cell also makes direct glycinergic synapses with certain RGCs, but it is not well established how many types receive this direct AII input. Here, we investigated functional AII amacrine→RGC synaptic connections in the retina of the guinea pig (Cavia porcellus) by recording inhibitory currents from RGCs in the presence of ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) antagonists. This condition isolates a specific pathway through the AII amacrine cell that does not require iGluRs: cone→ON cone bipolar cell→AII amacrine cell→RGC. These recordings show that AII amacrine cells make direct synapses with OFF Alpha, OFF Delta and a smaller OFF transient RGC type that co-stratifies with OFF Alpha cells. However, AII amacrine cells avoid making synapses with numerous RGC types that co-stratify with the connected RGCs. Selective AII connections ensure that a privileged minority of RGC types receives direct input from the night-vision pathway, independent from OFF bipolar cell activity. Furthermore, these results illustrate the specificity of retinal connections, which cannot be predicted solely by co-stratification of dendrites and axons within the inner plexiform layer.
Keywords: AII amacrine cell; RRID: AB_2079751; RRID: AB_2307351; RRID: AB_2315776; RRID: AB_2536190; retina; retinal ganglion cells; rod bipolar cell; scotopic vision; synapse.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflicting interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Synaptic connections of the narrow-field, bistratified rod amacrine cell (AII) in the rabbit retina.J Comp Neurol. 1992 Nov 8;325(2):152-68. doi: 10.1002/cne.903250203. J Comp Neurol. 1992. PMID: 1460111
-
Functional allocation of synaptic contacts in microcircuits from rods via rod bipolar to AII amacrine cells in the mouse retina.J Comp Neurol. 2013 Oct 15;521(15):3541-55. doi: 10.1002/cne.23370. J Comp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23749582 Free PMC article.
-
Microcircuitry of bipolar cells in cat retina.J Neurosci. 1984 Dec;4(12):2920-38. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-12-02920.1984. J Neurosci. 1984. PMID: 6502212 Free PMC article.
-
Development of On and Off retinal pathways and retinogeniculate projections.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004 Jan;23(1):31-51. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2003.10.001. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004. PMID: 14766316 Review.
-
Intrinsic properties and functional circuitry of the AII amacrine cell.Vis Neurosci. 2012 Jan;29(1):51-60. doi: 10.1017/S0952523811000368. Vis Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22310372 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electrical Coupling of Heterotypic Ganglion Cells in the Mammalian Retina.J Neurosci. 2020 Feb 5;40(6):1302-1310. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1374-19.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 2. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31896668 Free PMC article.
-
Using optogenetics to dissect rod inputs to OFF ganglion cells in the mouse retina.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2023;3:1146785. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2023.1146785. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37426783 Free PMC article.
-
Connectomic analysis reveals an interneuron with an integral role in the retinal circuit for night vision.Elife. 2020 May 15;9:e56077. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56077. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32412412 Free PMC article.
-
Glycinergic Inhibition Targets Specific Off Cone Bipolar Cells in Primate Retina.eNeuro. 2021 Feb 24;8(1):ENEURO.0432-20.2020. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0432-20.2020. Print 2021 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2021. PMID: 33188005 Free PMC article.
-
Dendro-somatic synaptic inputs to ganglion cells contradict receptive field and connectivity conventions in the mammalian retina.Curr Biol. 2022 Jan 24;32(2):315-328.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.11.005. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 34822767 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

