Complexity analysis of cortical surface detects changes in future Alzheimer's disease converters
- PMID: 28856799
- PMCID: PMC5745046
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.23773
Complexity analysis of cortical surface detects changes in future Alzheimer's disease converters
Abstract
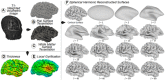
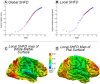
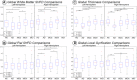
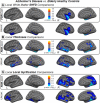
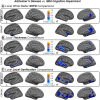
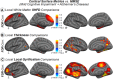
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurological disorder that creates neurodegenerative changes at several structural and functional levels in human brain tissue. The fractal dimension (FD) is a quantitative parameter that characterizes the morphometric variability of the human brain. In this study, we investigate spherical harmonic-based FD (SHFD), thickness, and local gyrification index (LGI) to assess whether they identify cortical surface abnormalities toward the conversion to AD. We study 33 AD patients, 122 mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients (50 MCI converters and 29 MCI nonconverters), and 32 healthy controls (HC). SHFD, thickness, and LGI methodology allowed us to perform not only global level but also local level assessments in each cortical surface vertex. First, we found that global SHFD decreased in AD and future MCI converters compared to HC, and in MCI converters compared to MCI nonconverters. Second, we found that local white matter SHFD was reduced in AD compared to HC and MCI mainly in medial temporal lobe. Third, local white-matter SHFD was significantly reduced in MCI converters compared to MCI nonconverters in distributed areas, including the medial frontal lobe. Thickness and LGI metrics presented a reduction in AD compared to HC. Thickness was significantly reduced in MCI converters compared to healthy controls in entorhinal cortex and lateral temporal. In summary, SHFD was the only surface measure showing differences between MCI individuals that will convert or remain stable in the next 4 years. We suggest that SHFD may be an optimal complement to thickness loss analysis in monitoring longitudinal changes in preclinical and clinical stages of AD. Hum Brain Mapp 38:5905-5918, 2017. © 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; fractal dimension; gyrification index; mild cognitive impairment; spherical harmonics; thickness.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Aguado C, Martínez J, Onís M (2000): Adaptation and validation in Spanish of the abbreviated version of the “Geriatric Depression Scale” (GDS) of Yesavage (in Spanish). Atención Primaria 26:328.
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995): Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc 57:289–300.
-
- Blanc F, Colloby SJ, Philippi N, De Pétigny X, Jung B, Demuynck C, Phillipps C, Anthony P, Thomas A, Bing F, Lamy J, Martin‐Hunyadi C, O'Brien JT, Cretin B, McKeith I, Armspach JP, Taylor JP (2015): Cortical thickness in dementia with lewy bodies and alzheimer's disease: A comparison of prodromal and dementia stages. PLoS One 10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chung MK, Robbins SM, Dalton KM, Davidson RJ, Alexander AL, Evans AC (2005): Cortical thickness analysis in autism with heat kernel smoothing. NeuroImage 25:1256–1265. - PubMed
-
- Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI (1999): Cortical surface‐based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage 9:179–194. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9931268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

