Inhibition of human cytochromes P450 2A6 and 2A13 by flavonoids, acetylenic thiophenes and sesquiterpene lactones from Pluchea indica and Vernonia cinerea
- PMID: 28856944
- PMCID: PMC6009911
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2017.1363741
Inhibition of human cytochromes P450 2A6 and 2A13 by flavonoids, acetylenic thiophenes and sesquiterpene lactones from Pluchea indica and Vernonia cinerea
Abstract
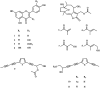
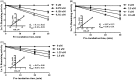
The human liver cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2A6 and the respiratory CYP2A13 enzymes play role in nicotine metabolism and activation of tobacco-specific nitrosamine carcinogens. Inhibition of both enzymes could offer a strategy for smoking abstinence and decreased risks of respiratory diseases and lung cancer. In this study, activity-guided isolation identified four flavonoids 1-4 (apigenin, luteolin, chrysoeriol, quercetin) from Vernonia cinerea and Pluchea indica, four hirsutinolide-type sesquiterpene lactones 5-8 from V. cinerea, and acetylenic thiophenes 9-11 from P. indica that inhibited CYP2A6- and CYP2A13-mediated coumarin 7-hydroxylation. Flavonoids were most effective in inhibition against CYP2A6 and CYP2A13, followed by thiophenes, and hirsutinolides. Hirsutinolides and thiophenes exhibited mechanism-based inhibition and in irreversible mode against both enzymes. The inactivation kinetic KI values of hirsutinolides against CYP2A6 and CYP2A13 were 5.32-15.4 and 0.92-8.67 µM, respectively, while those of thiophenes were 0.11-1.01 and 0.67-0.97 µM, respectively.
Keywords: CYP2A13; CYP2A6; acetylenic thiophenes; flavonoids; sesquiterpene lactones.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO global report on trends in prevalence of tobacco smoking 2015. Geneva, Switzerland; WHO; 2015.
-
- Su T, Bao Z, Zhang QY, et al. Human cytochrome P450 CYP2A13: predominant expression in the respiratory tract and its high efficiency metabolic activation of a tobacco-specific carcinogen, 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone. Cancer Res 2000;60:5074–9. - PubMed
-
- Jalas J, Hecht S, Murphy S.. Cytochrome P450 enzymes as catalysts of metabolism of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone, a tobacco specific carcinogen. Chem Res Toxicol 2005;18:95–110. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
