Competitive Antagonism of Anesthetic Action at the γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor by a Novel Etomidate Analog with Low Intrinsic Efficacy
- PMID: 28857763
- PMCID: PMC5645246
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001840
Competitive Antagonism of Anesthetic Action at the γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor by a Novel Etomidate Analog with Low Intrinsic Efficacy
Abstract
Background: The authors characterized the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor pharmacology of the novel etomidate analog naphthalene-etomidate, a potential lead compound for the development of anesthetic-selective competitive antagonists.
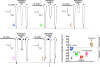
Methods: The positive modulatory potencies and efficacies of etomidate and naphthalene-etomidate were defined in oocyte-expressed α1β3γ2L γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors using voltage clamp electrophysiology. Using the same technique, the ability of naphthalene-etomidate to reduce currents evoked by γ-aminobutyric acid alone or γ-aminobutyric acid potentiated by etomidate, propofol, pentobarbital, and diazepam was quantified. The binding affinity of naphthalene-etomidate to the transmembrane anesthetic binding sites of the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor was determined from its ability to inhibit receptor photoaffinity labeling by the site-selective photolabels [H]azi-etomidate and R-[H]5-allyl-1-methyl-5-(m-trifluoromethyl-diazirynylphenyl) barbituric acid.
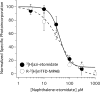
Results: In contrast to etomidate, naphthalene-etomidate only weakly potentiated γ-aminobutyric acid-evoked currents and induced little direct activation even at a near-saturating aqueous concentration. It inhibited labeling of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors by [H]azi-etomidate and R-[H]5-allyl-1-methyl-5-(m-trifluoromethyl-diazirynylphenyl) barbituric acid with similar half-maximal inhibitory concentrations of 48 μM (95% CI, 28 to 81 μM) and 33 μM (95% CI, 20 to 54 μM). It also reduced the positive modulatory actions of anesthetics (propofol > etomidate ~ pentobarbital) but not those of γ-aminobutyric acid or diazepam. At 300 μM, naphthalene-etomidate increased the half-maximal potentiating propofol concentration from 6.0 μM (95% CI, 4.4 to 8.0 μM) to 36 μM (95% CI, 17 to 78 μM) without affecting the maximal response obtained at high propofol concentrations.
Conclusions: Naphthalene-etomidate is a very low-efficacy etomidate analog that exhibits the pharmacology of an anesthetic competitive antagonist at the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None.
Figures




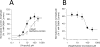
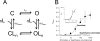
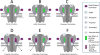
References
-
- Brull SJ, Kopman AF. Current Status of Neuromuscular Reversal and Monitoring: Challenges and Opportunities. Anesthesiology. 2017;126:173–190. - PubMed
-
- Kakisis JD, Antonopoulos CN, Moulakakis KG, Schneider F, Geroulakos G, Ricco JB. Protamine Reduces Bleeding Complications without Increasing the Risk of Stroke after Carotid Endarterectomy: A Meta-analysis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016;52:296–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

