Identification of miR-16 as an endogenous reference gene for the normalization of urinary exosomal miRNA expression data from CKD patients
- PMID: 28859135
- PMCID: PMC5578666
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183435
Identification of miR-16 as an endogenous reference gene for the normalization of urinary exosomal miRNA expression data from CKD patients
Abstract
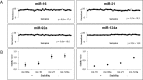
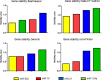
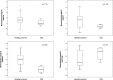
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a severe disorder with an increasing incidence worldwide. An early detection may help to prevent its progression and to minimize the risk of cardiovascular diseases as one of the major comorbidities. Recently, extracellular miRNAs like urinary exosomal miRNAs became of great interest as non-invasive biomarkers which can be determined by RT-qPCR. But until now, there is no consensus regarding the normalization of miRNAs isolated from body fluids. The present study analyzed the miRNAs miR-16, miR-92a, miR-21, miR-124a and the small nuclear RNA RNU6B for their applicability as an endogenous reference gene in expression studies of exosomal miRNAs isolated from CKD patients. For this purpose, miRNA expression levels were determined by RT-qPCR after the isolation of urinary exosomes from 33 CKD patients and from 5 healthy controls. Expression data was analyzed with the normalization determination software NormFinder, BestKeeper, GeNorm and DeltaCt. Our results revealed an abundant expression of the four candidate miRNAs in urinary exosomes and no detectable expression of RNU6B. We identified miR-16 as the most stable endogenous reference gene in our data set, making it a suitable endogenous reference gene for miRNA studies of urinary exosomes derived from CKD patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Brück K, Stel VS, Gambaro G, Hallan S, Völzke H, Ärnlöv J, et al. CKD Prevalence Varies across the European General Population. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2015. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015050542 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wiggins R. The spectrum of podocytopathies: A unifying view of glomerular diseases. Kidney International. 2007; 71: 1205–1214. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002222 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kriz W. Podocyte is the major culprit accounting for the progression of chronic renal disease. Microsc Res Tech. 2002; 57: 189–195. doi: 10.1002/jemt.10072 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fukuda A, Wickman LT, Venkatareddy MP, Wang SQ, Chowdhury MA, Wiggins JE, et al. Urine podocin:nephrin mRNA ratio (PNR) as a podocyte stress biomarker. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012; 27: 4079–4087. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs313 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY, Huang KH, Lee MJ, et al. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem. 2010; 56: 1733–1741. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2010.147405 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

