IL-17 in the lung: the good, the bad, and the ugly
- PMID: 28860146
- PMCID: PMC6048455
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00344.2017
IL-17 in the lung: the good, the bad, and the ugly
Abstract
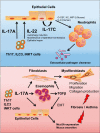
The IL-17 family of cytokines has emerged over the last two decades as a pleiotropic group of molecules that function in a wide variety of both beneficial and detrimental (pathological) processes, mainly in mucosal barrier tissue. The beneficial effects of IL-17 expression are especially important in the lung, where exposure to foreign agents is abundant. IL-17A plays an important role in protection from both extracellular bacteria and fungi, as well as viruses that infect cells of the mucosal tracts. IL-17 coregulated cytokines, such as IL-22, are involved in maintaining epithelial cell homeostasis and participate in epithelial cell repair/regeneration following inflammatory insults. Thus, the IL-17/IL-22 axis is important in both responding to, and recovering from, pathogens. However, aberrant expression or overexpression of IL-17 cytokines contributes to a number of pathological outcomes, including asthma, pneumonitis, and generation or exacerbation of pulmonary fibrosis. This review covers the good, bad, and ugly aspects of IL-17 in the lung.
Keywords: IL-17; IL-22; asthma; fibrosis; neutrophils.
Figures
References
-
- Aden K, Rehman A, Falk-Paulsen M, Secher T, Kuiper J, Tran F, Pfeuffer S, Sheibani-Tezerji R, Breuer A, Luzius A, Jentzsch M, Häsler R, Billmann-Born S, Will O, Lipinski S, Bharti R, Adolph T, Iovanna JL, Kempster SL, Blumberg RS, Schreiber S, Becher B, Chamaillard M, Kaser A, Rosenstiel P. Epithelial IL-23R signaling licenses protective IL-22 responses in intestinal inflammation. Cell Reports 16: 2208–2218, 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.054. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrews K, Ghosh MC, Schwingshackl A, Rapalo G, Luellen C, Waters CM, Fitzpatrick EA. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula is not associated with a switch to a Th2 response. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 310: L393–L402, 2016. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00305.2015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basha HI, Ramachandran S, Tiriveedhi V, Takenaka M, Subramanian V, Nath DS, Benshoff N, Patterson GA, Mohanakumar T. Critical role for IL-17A/F in the immunopathogenesis of obliterative airway disease induced by anti-MHC I antibodies. Transplantation 95: 293–300, 2013. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3182772244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

