Comparative Analyses of Signature Genes in Acute Rejection and Operational Tolerance
- PMID: 28860953
- PMCID: PMC5577301
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2017.17.4.237
Comparative Analyses of Signature Genes in Acute Rejection and Operational Tolerance
Abstract
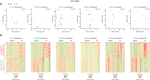
Using biomarkers as prediction tools or therapeutic targets can be a valuable strategy in transplantation. Recent studies identified biomarkers of acute rejection (AR) and operational tolerance (TOL) through the application of meta-analysis. In this study, we comparatively analyzed the signature genes in acute rejection and operational tolerance seen in human allogeneic transplantations using massive bioinformatical meta-analysis. To identify the signature genes in opposite immunological conditions, AR and TOL, we first collected the 1,252 gene expression data specifically intended for those circumstances. Then we excluded based on biological cut-values, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) as well as Multi-Dimensional Scaling (MDS). Using differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from meta-analysis, we then applied a ranked scoring system to identify the signature genes of AR and TOL. We identified 53 up-regulated and 32 down-regulated signature genes in acute rejection condition. Among them, ISG20, CXCL9, CXCL10, CCL19, FCER1G, PMSE1, UBD are highly expressed in AR condition. In operational tolerance, we identified 110 up-regulated and 48 down-regulated signature genes. TCL1A, BLNK, MS4A1, EBF1, IGHM are up-regulated in TOL condition. These genes are highly representative of AR or TOL across the different organs such as liver, kidney and heart. Since immune response is the sum of complex biological and molecular dynamics, these signature genes as well as pathway analysis using a systems biology approach could be used to catch the insights of the certain pathways that would be overlooked with the conventional gene-level comparative analysis.
Keywords: Graft rejection; Signature genes; Systems biology; Transplantation tolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

