Integrated RNA Sequencing and QTL Mapping to Identify Candidate Genes from Oryza rufipogon Associated with Salt Tolerance at the Seedling Stage
- PMID: 28861103
- PMCID: PMC5559499
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01427
Integrated RNA Sequencing and QTL Mapping to Identify Candidate Genes from Oryza rufipogon Associated with Salt Tolerance at the Seedling Stage
Abstract
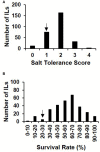
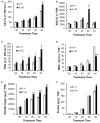
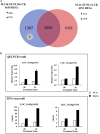
Soil salinity is a common abiotic stress affecting crop productivity. To identify favorable alleles from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) that enhance salinity tolerance of rice (O. sativa L.), a set of introgression lines (ILs) were developed. The ILs were derived from an O. rufipogon accession collected from Chaling (Hunan Province, China) as the donor, and a widely grown O. sativa indica cultivar 93-11 as the recipient. Through evaluating the salt tolerance of 285 ILs at the seedling stage, a total of 10 quantitative trait loci (QTLs) related to salt tolerance were identified on chromosomes 1, 5, 7 and 9-12, with individual QTLs explaining 2-8% of phenotypic variance. The O. rufipogon-derived alleles at four QTLs improved salt tolerance in the 93-11 background. At the same time, a salt-tolerant IL, 9L136, was identified and characterized. Compared with the recipient parent 93-11, a total of 1,391 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were detected specifically in 9L136 between salt stress and normal condition through genome-wide expression analysis. Of these, four DEGs located in the QTL regions carried by 9L136, suggesting that the four genes might be candidates associated with salt tolerance. Both the highly salt-tolerant ILs and the favorable O. rufipogon-derived QTLs identified in the present study will provide new genetic resources for improving the resistance of cultivated rice against salinity stress using molecular breeding strategies in the future.
Keywords: QTL analysis; RNA-seq; common wild rice; introgression line; salt tolerance; seedling stage.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with salt tolerance at seedling stage from Oryza rufipogon.J Genet Genomics. 2011 Dec 20;38(12):593-601. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2011.11.005. Epub 2011 Nov 30. J Genet Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22196402
-
Construction of introgression lines carrying wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) segments in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) background and characterization of introgressed segments associated with yield-related traits.Theor Appl Genet. 2006 Feb;112(3):570-80. doi: 10.1007/s00122-005-0165-2. Epub 2005 Dec 6. Theor Appl Genet. 2006. PMID: 16331476
-
Genetic Dissection of Seedling Stage Salinity Tolerance in Rice Using Introgression Lines of a Salt Tolerant Landrace Nona Bokra.J Hered. 2017 Sep 1;108(6):658-670. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esx067. J Hered. 2017. PMID: 28821187
-
Salt tolerance in rice: seedling and reproductive stage QTL mapping come of age.Theor Appl Genet. 2021 Nov;134(11):3495-3533. doi: 10.1007/s00122-021-03890-3. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Theor Appl Genet. 2021. PMID: 34287681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances and Challenges in the Breeding of Salt-Tolerant Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 9;21(21):8385. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218385. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33182265 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A genome-wide association study reveals the quantitative trait locus and candidate genes that regulate phosphate efficiency in a Vietnamese rice collection.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2020 Nov;26(11):2267-2281. doi: 10.1007/s12298-020-00902-2. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2020. PMID: 33268928 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Candidate Genes for a Major Quantitative Disease Resistance Locus From Soybean PI 427105B for Resistance to Phytophthora sojae.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 14;13:893652. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.893652. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35774827 Free PMC article.
-
Salt tolerance involved candidate genes in rice: an integrative meta-analysis approach.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Oct 1;20(1):452. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02679-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 33004003 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Candidate Genes for Salt Tolerance at the Seedling Stage Using Integrated Genome-Wide Association Study and Transcriptome Analysis in Rice.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 21;12(6):1401. doi: 10.3390/plants12061401. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36987089 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic dissection of foxtail millet bristles using combined QTL mapping and RNA-seq.Theor Appl Genet. 2025 Jan 23;138(1):33. doi: 10.1007/s00122-025-04820-3. Theor Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 39847146
References
-
- Akbar M., Yabuno T., Nakao S. (1972). Breeding for saline-resistant varieties of rice variability for salt tolerance among some rice varieties. Jpn. J. Breed. 22 277–284. 10.1270/jsbbs1951.22.277 - DOI
-
- Chen H. T., Jiang H., Yan M. X., Dong G. J., Qian Q., Guo L. B. (2008). QTL-mapping comparison of tolerance to alkali at germination period and early seedling stage between two different double haploid populations in rice. Mol. Plant Breed. 6 439–450.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

