MIR-519d suppresses the gastric cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Twist1 and inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- PMID: 28861156
- PMCID: PMC5575179
MIR-519d suppresses the gastric cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Twist1 and inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Abstract
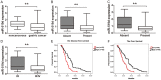
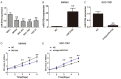
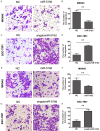
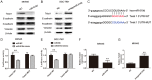
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) deregulation is frequent in human gastric cancer (GC). MiR-519d has been reported to function as tumor suppressor microRNA in some tumors. However, the role of miR-519d in GC progression remains unclear. In the study, we demonstrated that the expression of miR-519d was down-regulated in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines, and lower miR-519d expression was associated with distant metastasis, lymph node metastasis and clinical stage for patients with GC. Univariate and multivariate Cox analysis showed that lower miR-519d expression was positively associated with shorter disease-free survival (DFS) and the over survival (OS) time for GC patients and was an independent predictor. Kaplan-Meier curve and log-rank test also demonstrated that lower miR-519d had a poor shorter DFS and OS for GC patients. Function analysis showed that the inhibition of miR-519d expression was able to promote the cell proliferation, migration and invasion and over-expression of miR-519d in GC cells had inhibited effects. Moreover, we demonstrated that over-expression of miR-519d significantly inhibited the process of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) in GC cells and miR-519d can directly target at 3'-untranslation region of Twist1 and regulate its expression. We also demonstrated that miR-519d could suppress the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in GC cells. In vivo, we showed that miR-519d inhibited the tumor growth. Thus, our results suggested that miR-519d functioned as a tumor suppressor in GC and could be a promising therapeutic target for GC.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; Twist1; cell invasion; epithelial mesenchymal transition; miR-519d.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
