Inhibitory effect of tenomodulin versus ranibizumab on in vitro angiogenesis
- PMID: 28861344
- PMCID: PMC5554837
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2017.08.04
Inhibitory effect of tenomodulin versus ranibizumab on in vitro angiogenesis
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate anti-angiogenic effect of tenomodulin (TNMD) and ranibizumab on cell proliferation and capillary-like morphogenesis of vascular endothelial cells under the stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in vitro.
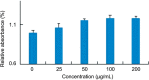
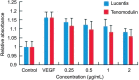
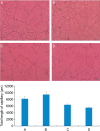
Methods: The effects of TNMD and ranibizumab on VEGF-induced proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were evaluated by MTT assay, and the effects of TNMD and ranibizumab on capillary-like structures formed by HUVECs under the stimulation of VEGF were examined in culture. Capillary-like morphogenesis of HUVECs was quantitatively evaluated, and total lengths of tube-like structures per field were measured in a masked way.
Results: HUVECs with both ranibizumab and TNMD protein showed MTT reduction in VEGF-stimulated cell proliferation as expected, while MTT absorbance in the HUVECs with TNMD was significantly declined than that with ranibizumab (P<0.01). The capillary-like structures formed by HUVECs were markedly impaired by the presence of both TNMD and ranibizumab in the culture medium. The total length of the capillary-like structures per field was significantly shorter in the medium with TNMD than that of ranibizumab (P<0.01). The inhibitory effect of TNMD on tube formation in vitro angiogenesis was significantly stronger than that of ranibizumab.
Conclusion: TNMD may have stronger inhibitory effect than ranibizumab on in vitro angiogenesis.
Keywords: angiogenesis; inhibitory effect; proliferation; ranibizumab; tenomodulin.
Figures
References
-
- Berg K, Pedersen TR, Sandvik L, Bragadottir R. Comparison of ranibizumab and bevacizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration according to the LUCAS treat-and-extend protocol. Ophthalmology. 2015;122(1):146–152. - PubMed
-
- Barquet LA. Role of VEGF in diseases of the retina. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2015;90(Suppl 1):3–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
