Better glycaemic control and less hypoglycaemia with insulin glargine 300 U/mL vs glargine 100 U/mL: 1-year patient-level meta-analysis of the EDITION clinical studies in people with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 28862801
- PMCID: PMC5836995
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.13105
Better glycaemic control and less hypoglycaemia with insulin glargine 300 U/mL vs glargine 100 U/mL: 1-year patient-level meta-analysis of the EDITION clinical studies in people with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the efficacy and safety of insulin glargine 300 U/mL (Gla-300) vs insulin glargine 100 U/mL (Gla-100) over 12 months in a patient-level meta-analysis, using data from the EDITION studies in people with type 2 diabetes (T2DM).
Methods: EDITION 1, 2 and 3 were multicentre, randomized, open-label, 2-arm, parallel-group, treat-to-target phase IIIa studies. Similar study designs and endpoints enabled a meta-analysis to be conducted.
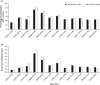
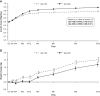
Results: Reductions in glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) were better sustained over 12 months with Gla-300 than with Gla-100 (least squares [LS] mean difference in change from baseline: -0.10 % [95% confidence interval {CI} -0.18 to -0.02] or -1.09 mmol/mol [95% CI -2.01 to -0.20]; P = .0174). Risk of confirmed (≤3.9 mmol/L) or severe hypoglycaemia was 15% lower with Gla-300 vs Gla-100 at night (relative risk 0.85 [95% CI 0.77-0.92]) and 6% lower at any time of day (relative risk 0.94 [95% CI 0.90-0.98]). Rates of hypoglycaemia were 18% lower with Gla-300 vs Gla-100 at night (rate ratio 0.82 [95% CI 0.67-0.99]), but comparable at any time of day. HbA1c <7.0 % without nocturnal hypoglycaemia was achieved by 24% more participants with Gla-300 than with Gla-100 (relative risk 1.24 [95% CI 1.03-1.50]). Severe hypoglycaemia was rare; in both treatment groups the incidence of events at any time of day was ≤3.6%, while rates were ≤0.08 events per participant-year.
Conclusions: In a broad population of people with T2DM over 12 months, use of Gla-300 provided more sustained glycaemic control and significantly lower hypoglycaemia risk at night and at any time of day compared with Gla-100.
Keywords: glycaemic control; hypoglycaemia; insulin analogues; meta-analysis; phase III study; type 2 diabetes.
© 2017 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
R. Ritzel has served as a consultant for AstraZeneca, Merck (MSD), Novo Nordisk, Servier and Sanofi and on the speakers bureau for AstraZeneca, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Merck (MSD), Novartis, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi. R. Roussel has served on advisory panels for AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly and Physiogenex, as a board member for Janssen, Merck (MSD), Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and as a consultant for Eli Lilly, and has received research support from Amgen and Sanofi. A. G. has served as a consultant for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Sanofi and Takeda, has received research support from AstraZeneca and Merck (MSD), and has served on the speakers bureau for AstraZeneca. J. V. has received research support and served on the advisory panel and speakers bureau for Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck (MSD), Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi and Takeda. C. B.‐W. is an employee of Sanofi. H. Y.‐J. has served on the advisory panel for Eli Lilly, Merck (MSD) and Sanofi, and as a consultant for Eli Lilly and Sanofi.
Figures



References
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient‐centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(1):140–149. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly LA, Morris AD, Evans JM. Adherence to insulin and its association with glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. QJM. 2007;100(6):345–350. - PubMed
-
- Becker RH, Dahmen R, Bergmann K, Lehmann A, Jax T, Heise T. New insulin glargine 300 Units·mL−1 provides a more even activity profile and prolonged glycemic control at steady state compared with insulin glargine 100 Units·mL−1. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(4):637–643. - PubMed
-
- Bergenstal RM, Bailey TS, Rodbard D, et al. Comparison of insulin glargine 300 U/mL and 100 U/mL in adults with type 1 diabetes: continuous glucose monitoring profiles and variability using morning or evening injections. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(4):554–560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

