Fusion of Taq DNA polymerase with single-stranded DNA binding-like protein of Nanoarchaeum equitans-Expression and characterization
- PMID: 28863186
- PMCID: PMC5581180
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184162
Fusion of Taq DNA polymerase with single-stranded DNA binding-like protein of Nanoarchaeum equitans-Expression and characterization
Abstract
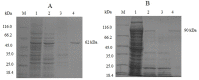
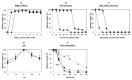
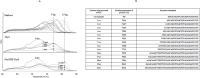
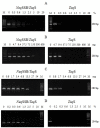
DNA polymerases are present in all organisms and are important enzymes that synthesise DNA molecules. They are used in various fields of science, predominantly as essential components for in vitro DNA syntheses, known as PCR. Modern diagnostics, molecular biology and genetic engineering need DNA polymerases which demonstrate improved performance. This study was aimed at obtaining a new NeqSSB-TaqS fusion DNA polymerase from the Taq DNA Stoffel domain and a single-stranded DNA binding-like protein of Nanoarchaeum equitans in order to significantly improve the properties of DNA polymerase. The DNA coding sequence of Taq Stoffel DNA polymerase and the nonspecific DNA-binding protein of Nanoarchaeum equitans (NeqSSB-like protein) were fused. A novel recombinant gene was obtained which was cloned into the pET-30 Ek/LIC vector and introduced into E. coli for expression. The recombinant enzyme was purified and its enzymatic properties including DNA polymerase activity, PCR amplification rate, thermostability, processivity and resistance to inhibitors, were tested. The yield of the target protein reached approximately 18 mg/l after 24 h of the IPTG induction. The specific activity of the polymerase was 2200 U/mg. The recombinant NeqSSB-TaqS exhibited a much higher extension rate (1000 bp template in 20 s), processivity (19 nt), thermostability (half-life 35 min at 95°C) and higher tolerance to PCR inhibitors (0.3-1.25% of whole blood, 0.84-13.5 μg of lactoferrin and 4.7-150 ng of heparin) than Taq Stoffel DNA polymerase. Furthermore, our studies show that NeqSSB-TaqS DNA polymerase has a high level of flexibility in relation to Mg2+ ions (from 1 to 5 mM) and KCl or (NH4)2SO4 salts (more than 60 mM and 40 mM, respectively). Using NeqSSB-TaqS DNA polymerase instead of the Taq DNA polymerase could be a better choice in many PCR applications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kaledin AS, Sliusarenko AG, Gorodetskiĭ SI. Isolation and properties of DNA polymerase from extreme thermophylic bacteria Thermus aquaticus YT-1. Biokhimiia. 1980; 45:644–651. - PubMed
-
- Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, et al. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988; 239:487–491. - PubMed
-
- Lawyer FC, Stoffel S, Saiki RK, Chang SY, Landre PA, Abramson RD, et al. High-level expression, purification, and enzymatic characterization of full-length Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase and a truncated form deficient in 5′ to 3′ exonuclease activity. PCR Methods Appl. 1993; 2:275–287. - PubMed
-
- Arezi B, Xing W, Sorge JA, Hogrefe HH. Amplification efficiency of thermostable DNA polymerases. Anal Biochem. 2003; 321:226–235. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

