The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 in Skin Carcinogenesis and Inflammation
- PMID: 28864076
- PMCID: PMC5742071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2017.07.847
The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 in Skin Carcinogenesis and Inflammation
Abstract
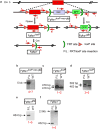
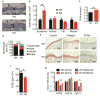
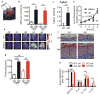
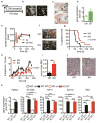
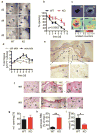
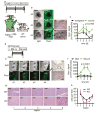
Fibroblast growth factor-binding protein 1 (FGFBP1) is a secreted chaperone that mobilizes paracrine-acting FGFs, stored in the extracellular matrix, and presents them to their cognate receptors. FGFBP1 enhances FGF signaling including angiogenesis during cancer progression and is upregulated in various cancers. Here we evaluated the contribution of endogenous FGFBP1 to a wide range of organ functions as well as to skin pathologies using Fgfbp1-knockout mice. Relative to wild-type littermates, knockout mice showed no gross pathologies. Still, in knockout mice a significant thickening of the epidermis associated with a decreased transepidermal water loss and increased proinflammatory gene expression in the skin was detected. Also, skin carcinogen challenge by 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene/12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate resulted in delayed and reduced papillomatosis in knockout mice. This was paralleled by delayed healing of skin wounds and reduced angiogenic sprouting in subcutaneous matrigel plugs. Heterozygous green fluorescent protein (GFP)-knock-in mice revealed rapid induction of gene expression during papilloma induction and during wound healing. Examination of wild-type skin grafted onto Fgfbp1 GFP-knock-in reporter hosts and bone marrow transplants from the GFP-reporter model into wild-type hosts revealed that circulating Fgfbp1-expressing cells migrate into healing wounds. We conclude that tissue-resident and circulating Fgfbp1-expressing cells modulate skin carcinogenesis and inflammation.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Aigner A, Ray PE, Czubayko F, Wellstein A. Immunolocalization of an FGF-binding protein reveals a widespread expression pattern during different stages of mouse embryo development. Histochem Cell Biol. 2002;117(1):1–11. - PubMed
-
- Anghelina M, Krishnan P, Moldovan L, Moldovan NI. Monocytes and macrophages form branched cell columns in matrigel: implications for a role in neovascularization. Stem Cells Dev. 2004;13(6):665–76. - PubMed
-
- Beer HD, Bittner M, Niklaus G, Munding C, Max N, Goppelt A, et al. The fibroblast growth factor binding protein is a novel interaction partner of FGF-7, FGF-10 and FGF-22 and regulates FGF activity: implications for epithelial repair. Oncogene. 2005;24(34):5269–77. - PubMed
-
- Czubayko F, Liaudet-Coopman ED, Aigner A, Tuveson AT, Berchem GJ, Wellstein A. A secreted FGF-binding protein can serve as the angiogenic switch in human cancer. Nat Med. 1997;3(10):1137–40. - PubMed
-
- Czubayko F, Smith RV, Chung HC, Wellstein A. Tumor-Growth and Angiogenesis Induced by a Secreted Binding-Protein for Fibroblast Growth-Factors. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(45):28243–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

