A frailty index from common clinical and laboratory tests predicts increased risk of death across the life course
- PMID: 28866737
- PMCID: PMC5636769
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-017-9993-7
A frailty index from common clinical and laboratory tests predicts increased risk of death across the life course
Abstract
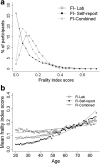
A frailty index (FI) based entirely on common clinical and laboratory tests might offer scientific advantages in understanding ageing and pragmatic advantages in screening. Our main objective was to compare an FI based on common laboratory tests with an FI based on self-reported data; we additionally investigated if the combination of subclinical deficits with clinical ones increased the ability of the FI to predict mortality. In this secondary analysis of the 2003-2004 and 2005-2006 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data, 8888 individuals aged 20+ were evaluated. Three FIs were constructed: a 36-item FI using self-reported questionnaire data (FI-Self-report); a 32-item FI using data from laboratory test values plus pulse and blood pressure measures (FI-Lab); and a 68-item FI that combined all items from each index (FI-Combined). The mean FI-Lab score was 0.15 ± 0.09, the FI-Self-report was 0.11 ± 0.11 and FI-Combined was 0.13 ± 0.08. Each index showed some typical FI characteristics (skewed distribution with long right tail, non-linear increase with age). Even so, there were fewer people with low frailty levels and a slower increase with age for the FI-Lab compared to the FI-Self-report. Higher frailty level was associated with higher risk of death, although it was strongest at older ages. Both FI-Lab and FI-Self-report remained significant in a combined model predicting death. The FI-Lab was feasible and valid, demonstrating that even subclinical deficit accumulation increased mortality risk. This suggests that deficit accumulation, from the subcellular to the clinically visible is a useful construct that may advance our understanding of the ageing process.
Keywords: Ageing; Biomarkers; Deficit accumulation; Frail elderly; Frailty; NHANES.
Conflict of interest statement
All participants signed written consent forms. Ethical approval for the NHANES study was given by the Institutional Review Board of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC 2014).
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm. Updated 2014
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous