Substance P and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide in the Glands of External Auditory Canal Skin
- PMID: 28866875
- PMCID: PMC5678038
- DOI: 10.21053/ceo.2017.00129
Substance P and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide in the Glands of External Auditory Canal Skin
Abstract
Objectives: The earwax (cerumen) that covers external auditory canal (EAC) skin contains a mixture of ceruminous and sebaceous gland substances, such as lipids, peptides, and proteins. The components secreted from the ceruminous gland that is a modified sweat gland form cerumen and contain several antimicrobial factors. Since substance P (SP) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), known as a secretagogue, have been found in sweat glands, our purpose was to determine the expression of SP and CGRP in the glands of EAC skin.
Methods: Sections of normal human EAC skins were immunostained for the presence of SP and CGRP using polyclonal antibodies. Immunoreactivity was detected using an avidin-biotin peroxidase complex method.
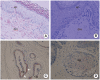
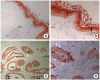
Results: SP staining was found in ceruminous gland acini and myoepithelial cells. But the SP staining was not found in the sebaceous glands and epidermal region. CGRP was strongly stained in the ceruminous gland and weakly in the sebaceous gland cells. Interestingly, most prominent staining of SP and CGRP was noted in the myoepithelial cells of the ceruminous gland.
Conclusion: The findings in this study suggest that SP and CGRP are expressed in the glands of the EAC skin and secreted in the process of ceruminous gland secretion.
Keywords: Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide; External Auditory Canal; Gland; Substance P.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Main T, Lim D. The human external auditory canal, secretory system: an ultrastructural study. Laryngoscope. 1976 Aug;86(8):1164–76. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa H. Immunocytological localization of lysozyme in human skin. J Dermatol. 1975 Mar;2(1):45–50. - PubMed
-
- Harder J, Bartels J, Christophers E, Schroder JM. A peptide antibiotic from human skin. Nature. 1997 Jun;387(6636):861. - PubMed
-
- Ali RS, Falconer A, Ikram M, Bissett CE, Cerio R, Quinn AG. Expression of the peptide antibiotics human beta defensin-1 and human beta defensin-2 in normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2001 Jul;117(1):106–11. - PubMed
-
- Yoon YJ, Park JW, Lee EJ. Presence of hBD-1 and hBD-2 in human cerumen and external auditory canal skin. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008 Aug;128(8):871–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

