Cystic Pancreatic Lymphangioma - Diagnostic Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound
- PMID: 28868471
- PMCID: PMC5580107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpge.2016.01.006
Cystic Pancreatic Lymphangioma - Diagnostic Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound
Abstract
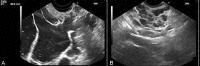
Pancreatic cystic lymphangiomas are rare benign lesions that arise from lymphatic vessels, accounting for less than 0.2% of all pancreatic cysts. Typically it is asymptomatic and discovery occurs during imaging exams for non-pancreatic disease. In the past, a definite diagnosis was made through surgery, with complete resection of all tumoral tissue to prevent recurrence. Nowadays, the development of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) made it possible to identify these cysts combining morphologic ultrasound features, macroscopic aspirated fluid appearance, biochemical and cytological evaluation of the sample. We report two cases of cystic pancreatic lymphangioma diagnosed through EUS, allowing conservative management without surgery. These cases show that cystic pancreatic lymphangioma should be considered in the differential diagnosis of cystic pancreatic lesions and that EUS is an important tool for their recognition.
Os linfangiomas quísticos pancreáticos são lesões benignas raras com origem em vasos linfáticos, correspondendo a menos de 0,2% da totalidade de quistos pancreáticos. Na maioria são assintomáticos sendo a sua descoberta incidental. Tradicionalmente o seu diagnóstico era cirúrgico, com completa ressecção de todo o tecido tumoral para prevenir recorrência. Actualmente, o desenvolvimento da ecoendoscopia (EUS) permitiu identificar estes quistos combinando as suas características ultrasonográficas, aparência macroscópica do fluido aspirado, e avaliação bioquímica e citológica da amostra. Os autores descrevem dois casos de linfangiomas quísticos pancreáticos diagnosticados por EUS, permitindo uma abordagem conservadora. Estes demonstram que os linfangiomas quísticos pancreáticos devem ser considerados no diagnóstico diferencial de lesões quísticas pancreáticas e que a EUS é importante no seu reconhecimento.
Keywords: Endosonography; Lymphangioma, Cystic; Pancreatic Neoplasms.
Figures




References
-
- Coe A.W., Evans J., Conway J. Pancreas cystic lymphangioma diagnosed with EUS-FNA. J Pancreas. 2012;13:282–2848. - PubMed
-
- Applebaum B., Cunningham J.T. Two cases of cystic lymphangioma of the pancreas. Endoscopy. 2006;38:E24–E25. - PubMed
-
- Fonseca R., Pitman M.B. Lymphangioma of the pancreas: a multimodal approach to pre-operative diagnosis. Cytopathology. 2013;24:172–176. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
