Familial interstitial pulmonary fibrosis in two different families in India: A case series
- PMID: 28869238
- PMCID: PMC5592765
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-2113.213824
Familial interstitial pulmonary fibrosis in two different families in India: A case series
Abstract
Introduction: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a chronic progressive interstitial lung disease (ILD), Occasionally, IPF occurs in families. Familial interstitial lung disease has been reported worldwide, limited information is available on the disease among Indian patients.
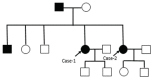
Case presentation: A 59-year-old woman presented with a 2-year history of progressive dyspnoea. Based on clinical and radiological features, our patient was diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Several family members of her first and second generations had died from respiratory failure. Her sister also diagnosed as IPF based on typical High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) finding though she was asymptomatic and came for screening. In addition, another male patient also had similar history and diagnosed as familial IPF based on HRCT and genetic testing in spite of significant occupational exposure. Genetic study revealed SFTPA1 gene was associated with susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Conclusion: Our report illustrates that asymptomatic screening of family member can uncover such a serious disease in patients with familial interstitial fibrosis. Otherwise, clinical, radiological, and histological features are indistinguishable from those of sporadic cases. Furthermore, our work highlights the importance of compiling a thorough family history in individuals presenting with cough and dyspnoea, particularly in younger patients identified with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Douglas WW, Ryu JH, Schroeder DR. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Impact of oxygen and colchicine, prednisone, or no therapy on survival. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161(4 Pt 1):1172–8. - PubMed
-
- Collard HR, Ryu JH, Douglas WW, Schwarz MI, Curran-Everett D, King TE, Jr, et al. Combined corticosteroid and cyclophosphamide therapy does not alter survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2004;125:2169–74. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Brown KK, Bradford WZ, Starko K, Noble PW, Schwartz DA, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of interferon gamma-1bin patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:125–33. - PubMed
-
- Gross TJ, Hunninghake GW. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:517–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

