Human-monoclonal-antibody therapy protects nonhuman primates against advanced Lassa fever
- PMID: 28869611
- PMCID: PMC5719877
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.4396
Human-monoclonal-antibody therapy protects nonhuman primates against advanced Lassa fever
Abstract
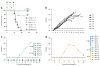
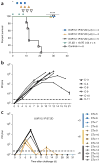
There are no approved treatments for Lassa fever, which is endemic to the same regions of West Africa that were recently devastated by Ebola. Here we show that a combination of human monoclonal antibodies that cross-react with the glycoproteins of all four clades of Lassa virus is able to rescue 100% of cynomolgus macaques when treatment is initiated at advanced stages of disease, including up to 8 d after challenge.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: details are available in the online version of the paper.
Figures
References
-
- McCormick JB, Webb PA, Krebs JW, Johnson KM, Smith ES. J Infect Dis. 1987;155:437–444. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. [Accessed 5 July 2017];Lassa Fever – Nigeria. Available at: http://www.who.int/csr/don/28-june-2017-lassa-fever-nigeria/en/
-
- Schmitz H, et al. Microbes Infect. 2002;4:43–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

