Herbal Medicine for Xerostomia in Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 28870110
- PMCID: PMC6041902
- DOI: 10.1177/1534735417728336
Herbal Medicine for Xerostomia in Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Background: Xerostomia (dry mouth) causes many clinical problems, including oral infections, speech difficulties, and impaired chewing and swallowing of food. Many cancer patients have complained of xerostomia induced by cancer therapy.
Objective: The aim of this systematic review is to assess the efficacy of herbal medicine for the treatment of xerostomia in cancer patients.
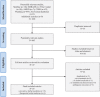
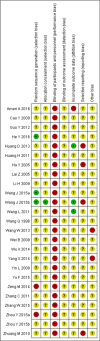
Materials and methods: Randomized controlled trials investigating the use of herbal medicines to treat xerostomia in cancer patients were included. We searched the following 12 databases without restrictions on time or language. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool.
Results: Twenty-five randomized controlled trials involving 1586 patients met the inclusion criteria. A total of 24 formulas were examined in the included trials. Most of the included trials were insufficiently reported in the methodology section. Five formulas were shown to significantly improve the salivary flow rate compared to comparators. Regarding the grade of xerostomia, all formulas with the exception of a Dark Plum gargle solution with normal saline were significantly effective in reducing the severity of dry mouth. Adverse events were reported in 4 trials, and adverse effects of herbal medicine were reported in 3 trials.
Conclusions: We found herbal medicines had potential benefits for improving salivary function and reducing the severity of dry mouth in cancer patients. However, methodological limitations and a relatively small sample size reduced the strength of the evidence. More high-quality trials reporting sufficient methodological data are warranted to enforce the strength of evidence regarding the effectiveness of herbal medicines.
Keywords: herbal medicine; randomized controlled trials; review; traditional East Asian medicine; xerostomia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
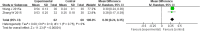
References
-
- Napenas JJ, Brennan MT, Fox PC. Diagnosis and treatment of xerostomia (dry mouth). Odontology. 2009;97:76-83. - PubMed
-
- Bhide SA, Miah AB, Harrington KJ, Newbold KL, Nutting CM. Radiation-induced xerostomia: pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2009;21:737-744. - PubMed
-
- Visvanathan V, Nix P. Managing the patient presenting with xerostomia: a review. Int J Clin Pract. 2010;64:404-407. - PubMed
-
- Villa A, Wolff A, Aframian D, et al. World Workshop on Oral Medicine VI: a systematic review of medication-induced salivary gland dysfunction: prevalence, diagnosis, and treatment. Clin Oral Investig. 2015;19:1563-1580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

