The DLGAP family: neuronal expression, function and role in brain disorders
- PMID: 28870203
- PMCID: PMC5583998
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-017-0324-9
The DLGAP family: neuronal expression, function and role in brain disorders
Abstract
The neurotransmitter glutamate facilitates neuronal signalling at excitatory synapses. Glutamate is released from the presynaptic membrane into the synaptic cleft. Across the synaptic cleft glutamate binds to both ion channels and metabotropic glutamate receptors at the postsynapse, which expedite downstream signalling in the neuron. The postsynaptic density, a highly specialized matrix, which is attached to the postsynaptic membrane, controls this downstream signalling. The postsynaptic density also resets the synapse after each synaptic firing. It is composed of numerous proteins including a family of Discs large associated protein 1, 2, 3 and 4 (DLGAP1-4) that act as scaffold proteins in the postsynaptic density. They link the glutamate receptors in the postsynaptic membrane to other glutamate receptors, to signalling proteins and to components of the cytoskeleton. With the central localisation in the postsynapse, the DLGAP family seems to play a vital role in synaptic scaling by regulating the turnover of both ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors in response to synaptic activity. DLGAP family has been directly linked to a variety of psychological and neurological disorders. In this review we focus on the direct and indirect role of DLGAP family on schizophrenia as well as other brain diseases.
Keywords: DLGAP1; DLGAP2; DLGAP3; DLGAP4; GKAP; PSD; SAPAP; Scaffold proteins; Schizophrenia; Synaptic scaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
AHR is a PhD student in the Cellular and Genetic Medicine Program. HBR is Associate Professor in the Department of Biomedical Sciences interested in molecular and cellular neurobiology, AS is Associate Professor in the Medical Genetics Program, Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. AS is interested in genomic organization, gene expression and gene regulatory mechanisms in the brain, DLGAP4 gene, cytogenetics.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
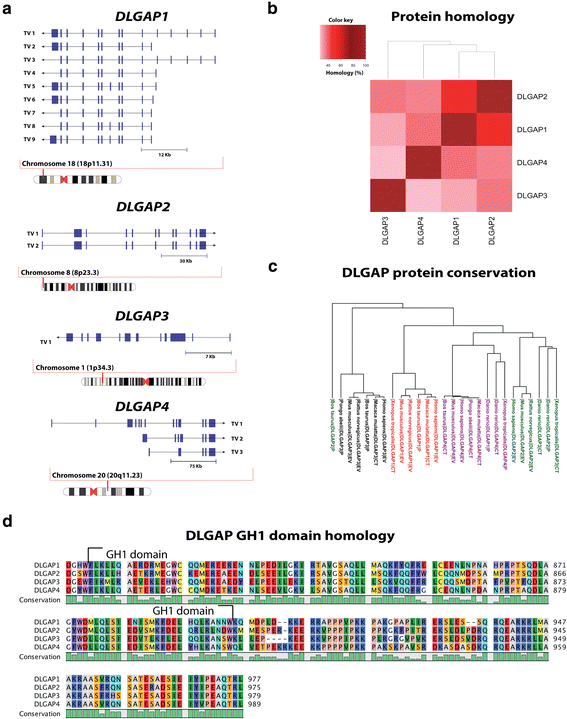
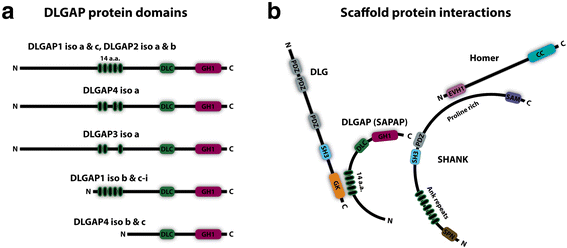

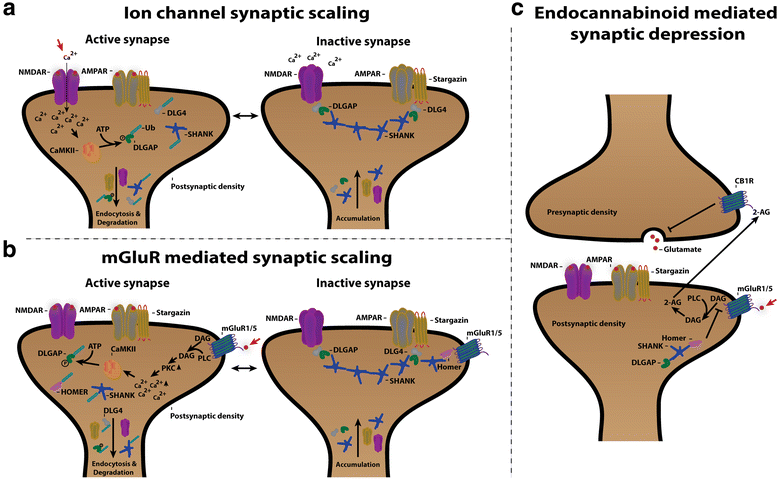
References
-
- Chen L, Chetkovich DM, Petralia RS, Sweeney NT, Kawasaki Y, Wenthold RJ, et al. Stargazin regulates synaptic targeting of AMPA receptors by two distinct mechanisms. Nature. Macmillian Magazines Ltd. 2000;408:936–943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

