Evaluation of consumer monitors to measure particulate matter
- PMID: 28871212
- PMCID: PMC5580935
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2017.02.013
Evaluation of consumer monitors to measure particulate matter
Abstract
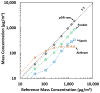
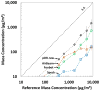
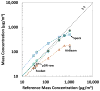
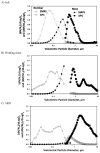
Recently, inexpensive (<$300) consumer aerosol monitors (CAMs) targeted for use in homes have become available. We evaluated the accuracy, bias, and precision of three CAMs (Foobot from Airoxlab, Speck from Carnegie Mellon University, and AirBeam from HabitatMap) for measuring mass concentrations in occupational settings. In a laboratory study, PM2.5 measured with the CAMs and a medium-cost aerosol photometer (personal DataRAM 1500, Thermo Scientific) were compared to that from reference instruments for three aerosols (salt, welding fume, and Arizona road dust, ARD) at concentrations up to 8500 μg/m3. Three of each type of CAM were included to estimate precision. Compared to reference instruments, mass concentrations measured with the Foobot (r-value = 0.99) and medium-cost photometer (r-value = 0.99) show strong correlation, whereas those from the Speck (r-value range 0.88 - 0.99) and AirBeam (0.7 - 0.96) were less correlated. The Foobot bias was (-12%) for ARD and measurements were similar to the medium-cost instrument. Foobot bias was (< -46%) for salt and welding fume aerosols. Speck bias was at 18% salt for ARD and -86% for welding fume. AirBeam bias was (-36%) for salt and (-83%) for welding fume. All three photometers had a bias (< -82%) for welding fume. Precision was excellent for the Foobot (coefficient of variation range: 5% to 8%) and AirBeam (2% to 9%), but poorer for the Speck (8% to 25%). These findings suggest that the Foobot, with a linear response to different aerosol types and good precision, can provide reasonable estimates of PM2.5 in the workplace after site-specific calibration to account for particle size and composition.
Keywords: AirBeam; Foobot; Low-cost monitors; PM2.5; Speck; environmental monitoring; occupational monitoring.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Respirable Mass Concentrations Measured by a Personal Dust Monitor and a Personal DataRAM to Gravimetric Measurements.Ann Work Expo Health. 2017 Dec 15;62(1):62-71. doi: 10.1093/annweh/wxx083. Ann Work Expo Health. 2017. PMID: 29136129 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of Four Consumer-grade Air Pollution Measurement Devices in Different Residences.Aerosol Air Qual Res. 2020 Feb;20(2):217-230. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2019.01.0045. Aerosol Air Qual Res. 2020. PMID: 33184562 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-comparison of Low-cost Sensors for Measuring the Mass Concentration of Occupational Aerosols.Aerosol Sci Technol. 2016;50(5):462-473. doi: 10.1080/02786826.2016.1162901. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Aerosol Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 28867868 Free PMC article.
-
Is electric arc welding linked to manganism or Parkinson's disease?Toxicol Rev. 2005;24(4):237-57. doi: 10.2165/00139709-200524040-00004. Toxicol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16499406 Review.
-
Development of an animal model to study the potential neurotoxic effects associated with welding fume inhalation.Neurotoxicology. 2006 Sep;27(5):745-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2006.01.009. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Neurotoxicology. 2006. PMID: 16546258 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a Portable Aerosol Collector and Spectrometer to measure particle concentration by composition and size.Aerosol Sci Technol. 2019 Jun 3;53(6):675-687. doi: 10.1080/02786826.2019.1600654. Aerosol Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 37736266 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Feasibility of a Future Integrated Larger-Scale Epidemiological Study to Evaluate Health Risks of Air Pollution Episodes in Children.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 12;19(14):8531. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19148531. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35886381 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in gravimetric correction factors for nephelometer-derived estimates of personal exposure to PM2.5.Environ Pollut. 2019 Jul;250:251-261. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.121. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Environ Pollut. 2019. PMID: 30999202 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Cost, Distributed Environmental Monitors for Factory Worker Health.Sensors (Basel). 2018 May 3;18(5):1411. doi: 10.3390/s18051411. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29751534 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of PM2.5 Concentration at University Transit Bus Stops Using Low-Cost Aerosol Monitors by Student Commuters.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 12;24(14):4520. doi: 10.3390/s24144520. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Airoxlab. Product specifications datasheet. 2016 Online source. http://foobot.io/foobotspecs.pdf.
-
- Alexander JM, Meland B, Laskina O, Young MA, Grassian VH, Kleiber PD. Light scattering from diatomaceous earth aerosol. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer. 2013;125:33–37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2013.04.013. - DOI
-
- Antonini JM, Taylor MD, Zimmer AT, Roberts JR. Pulmonary responses to welding fumes: role of metal constituents. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A. 2004;67(3):233–249. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti B, Fine PM, Delfino R, Sioutas C. Performance evaluation of the active-flow personal DataRAM PM 2.5 mass monitor (Thermo Anderson pDR-1200) designed for continuous personal exposure measurements. Atmospheric Environment. 2004;38(20):3329–3340.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
