Modeling continuous response variables using ordinal regression
- PMID: 28872693
- PMCID: PMC5675816
- DOI: 10.1002/sim.7433
Modeling continuous response variables using ordinal regression
Abstract
We study the application of a widely used ordinal regression model, the cumulative probability model (CPM), for continuous outcomes. Such models are attractive for the analysis of continuous response variables because they are invariant to any monotonic transformation of the outcome and because they directly model the cumulative distribution function from which summaries such as expectations and quantiles can easily be derived. Such models can also readily handle mixed type distributions. We describe the motivation, estimation, inference, model assumptions, and diagnostics. We demonstrate that CPMs applied to continuous outcomes are semiparametric transformation models. Extensive simulations are performed to investigate the finite sample performance of these models. We find that properly specified CPMs generally have good finite sample performance with moderate sample sizes, but that bias may occur when the sample size is small. Cumulative probability models are fairly robust to minor or moderate link function misspecification in our simulations. For certain purposes, the CPMs are more efficient than other models. We illustrate their application, with model diagnostics, in a study of the treatment of HIV. CD4 cell count and viral load 6 months after the initiation of antiretroviral therapy are modeled using CPMs; both variables typically require transformations, and viral load has a large proportion of measurements below a detection limit.
Keywords: nonparametric maximum likelihood estimation; ordinal regression model; rank-based statistics; semiparametric transformation model.
Copyright © 2017 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures



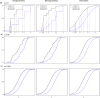



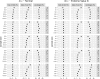
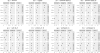




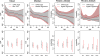

References
-
- Sall J. A monotone regression smoother based on ordinal cumulative logistic regression. ASA Proceedings of Statistical Computing Section. 1991:276–281.
-
- Harrell FE. Regression Modeling Strategies: With Applications to Linear Models, Logistic and Ordinal Regression, and Survival Analysis. Second. Springer; 2015.
-
- Walker SH, Duncan DB. Estimation of the probability of an event as a function of several independent variables. Biometrika. 1967;54(1–2):167–179. - PubMed
-
- McCullagh P. Regression models for ordinal data. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (Methodological) 1980;42(2):109–142.
-
- Fienberg SE. The Analysis of Cross-classified Categorical Data. Second. MIT Press; Cambridge, MA: 1980. (reprinted by Springer, New York, 2007)
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
