The readability of scientific texts is decreasing over time
- PMID: 28873054
- PMCID: PMC5584989
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.27725
The readability of scientific texts is decreasing over time
Abstract
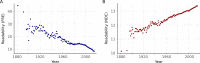
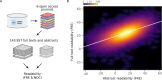
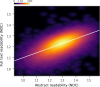
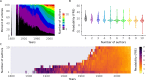
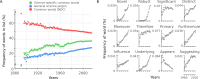
Clarity and accuracy of reporting are fundamental to the scientific process. Readability formulas can estimate how difficult a text is to read. Here, in a corpus consisting of 709,577 abstracts published between 1881 and 2015 from 123 scientific journals, we show that the readability of science is steadily decreasing. Our analyses show that this trend is indicative of a growing use of general scientific jargon. These results are concerning for scientists and for the wider public, as they impact both the reproducibility and accessibility of research findings.
Keywords: data analysis; jargon; metascience; readability; scientific communication.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures






References
-
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software. 2014;67:51
-
- Benjamin RG. Reconstructing readability: recent developments and recommendations in the analysis of text difficulty. Educational Psychology Review. 2012;24:63–88. doi: 10.1007/s10648-011-9181-8. - DOI
-
- Bird S, Klein E, Lower E, Loper E. Natural Language Processing with Python. Vol. 43. O’Reilly Media; 2009.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

