Ureter metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a case report
- PMID: 28874180
- PMCID: PMC5585961
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-017-1379-z
Ureter metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a case report
Abstract
Background: In most cases, prostate cancer metastasizes to the lymph nodes, bone, and liver. In very rare cases, it metastasizes to the ureter. Due to the difficulty in making a preoperative diagnosis, ureteral metastasis from prostate cancer is typically diagnosed after nephroureterectomy.
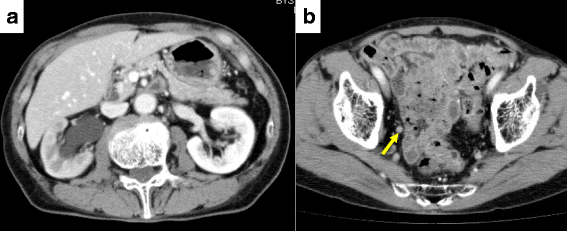
Case presentation: A 77-year-old Asian Japanese man with right hydronephrosis and hydroureter was referred to our hospital to undergo further examination due to the suspicion of ureteral cancer. He had been diagnosed 2 years previously with prostate cancer with a Gleason score of 4+5=9. He received radiotherapy and androgen deprivation therapy. A nephroureterectomy was performed for suspected right ureteral cancer. On the basis of a histopathological examination, poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma was suspected, and the tumor cells were positive for prostate-specific antigen immunohistochemically.
Conclusions: We herein report a rare case of ureteral metastasis in castration resistant prostate cancer.
Keywords: Female PSA; Skene’s gland adenocarcinoma; Skene’s gland cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the institutional review board of Yokohama City University Medical Center.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Disibio G, French SW. Metastatic patterns of cancers: results from a large autopsy study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008;132(6):931–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

