Do juveniles help or hinder? Influence of juvenile offspring on maternal behavior and reproductive outcomes in wild chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes)
- PMID: 28874268
- PMCID: PMC5659293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2017.07.012
Do juveniles help or hinder? Influence of juvenile offspring on maternal behavior and reproductive outcomes in wild chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes)
Abstract
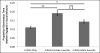
Compared to great apes, humans maintain a relatively rapid reproductive pace despite long periods of dependency. This seemingly contradictory set of traits is made possible by weaning offspring before nutritional independence and alloparents who help provide care. In traditional societies, this help may be provided to mothers in part by their juvenile offspring who carry, supervise, or provision younger siblings. In contrast to humans, chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) are nutritionally independent after weaning, yet juveniles continue to travel with their mother and younger sibling for an additional 4-5 years. This continued association could be costly to the mother if she continues to invest in weaned offspring. Alternately, while juvenile chimpanzees do not typically provision younger siblings, their presence and social interaction with infants may allow mothers to focus on other tasks. In this study, we investigate the costs and benefits to mothers of continued association with juveniles in wild chimpanzees. Using 26 years of long-term behavioral data we examined how maternal activity budgets varied based on the presence of a dependent juvenile offspring. We found that continued social interaction between mothers and juveniles does not influence the mother's time allocated to interacting with the younger infant, her feeding, resting, or travel time, or time socializing with other community members. Instead, mothers may benefit from the additional social interaction and/or relationship with their older offspring. Using 45 years of demographic data we found that those offspring who had an older sibling tended to be more likely to survive each year from birth to 8 years than those without an older sibling. Additionally, interbirth intervals were more likely to end when the female had an older offspring present. A mutually beneficial mother-juvenile dynamic in great apes provides insight into continued association between mothers and offspring after nutritional independence and the emergence of juvenile helping during hominin evolution.
Keywords: Life history; Mothers; Reproduction; Siblings.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Akaike H. Information theory as an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In: Petrov BN, Csaki F, editors. Second International Symposium on Information Theory. Akaemiai Kiado; Budapest: 1974. pp. 267–281.
-
- Albers PCH, de Vries H. Elo-rating as a tool in the sequential estimation of dominance strengths. Anim. Behav. 2001;61:489–495.
-
- Altmann J. Observational study of behavior: sampling methods. Behaviour. 1974;49:227–266. - PubMed
-
- Altmann J, Alberts SC. Intraspecific variability in fertility and offspring survival in a nonhuman primate: Behavioral control of ecological and social sources. In: Wachter KW, Bulatao RA, editors. Offspring: Human Fertility Behavior in Biodemographic Perspective. The National Academies Press; Washington D.C.: 2003. pp. 140–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

