Decidualisation and placentation defects are a major cause of age-related reproductive decline
- PMID: 28874785
- PMCID: PMC5585348
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00308-x
Decidualisation and placentation defects are a major cause of age-related reproductive decline
Abstract
Mammalian reproductive performance declines rapidly with advanced maternal age. This effect is largely attributed to the exponential increase in chromosome segregation errors in the oocyte with age. Yet many pregnancy complications and birth defects that become more frequent in older mothers, in both humans and mice, occur in the absence of karyotypic abnormalities. Here, we report that abnormal embryonic development in aged female mice is associated with severe placentation defects, which result from major deficits in the decidualisation response of the uterine stroma. This problem is rooted in a blunted hormonal responsiveness of the ageing uterus. Importantly, a young uterine environment can restore normal placental as well as embryonic development. Our data highlight the pivotal, albeit under-appreciated, impact of maternal age on uterine adaptability to pregnancy as major contributor to the decline in reproductive success in older females.Advanced maternal age has been associated with lower reproductive success and higher risk of pregnancy complications. Here the authors show that maternal ageing-related embryonic abnormalities in mouse are caused by decidualisation and placentation defects that can be rescued by transferring the embryo from an old to a young uterus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
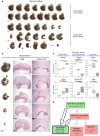
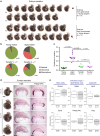
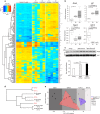
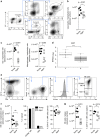

References
-
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Osterman MJ, Curtin SC, Matthews TJ. Births: final data for 2013. Natl. Vital Stat. Rep. 2015;64:1–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

