Effect of Fusidic Acid on the Kinetics of Molecular Motions During EF-G-Induced Translocation on the Ribosome
- PMID: 28874811
- PMCID: PMC5585275
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-10916-8
Effect of Fusidic Acid on the Kinetics of Molecular Motions During EF-G-Induced Translocation on the Ribosome
Abstract
The translocation step of protein synthesis entails binding and dissociation of elongation factor G (EF-G), movements of the two tRNA molecules, and motions of the ribosomal subunits. The translocation step is targeted by many antibiotics. Fusidic acid (FA), an antibiotic that blocks EF-G on the ribosome, may also interfere with some of the ribosome rearrangements, but the exact timing of inhibition remains unclear. To follow in real-time the dynamics of the ribosome-tRNA-EF-G complex, we have developed a fluorescence toolbox which allows us to monitor the key molecular motions during translocation. Here we employed six different fluorescence observables to investigate how FA affects translocation kinetics. We found that FA binds to an early translocation intermediate, but its kinetic effect on tRNA movement is small. FA does not affect the synchronous forward (counterclockwise) movements of the head and body domains of the small ribosomal subunit, but exerts a strong effect on the rates of late translocation events, i.e. backward (clockwise) swiveling of the head domain and the transit of deacylated tRNA through the E' site, in addition to blocking EF-G dissociation. The use of ensemble kinetics and numerical integration unraveled how the antibiotic targets molecular motions within the ribosome-EF-G complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
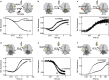
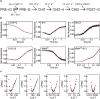
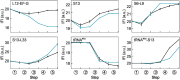
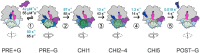
Similar articles
-
Fusidic acid targets elongation factor G in several stages of translocation on the bacterial ribosome.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 6;290(6):3440-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.611608. Epub 2014 Dec 1. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25451927 Free PMC article.
-
Perturbation of ribosomal subunit dynamics by inhibitors of tRNA translocation.RNA. 2021 Sep;27(9):981-990. doi: 10.1261/rna.078758.121. Epub 2021 Jun 11. RNA. 2021. PMID: 34117118 Free PMC article.
-
On the pathway of ribosomal translocation.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016 Nov;92:401-415. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.048. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016. PMID: 27431796
-
Structural insights into ribosome translocation.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Sep;7(5):620-36. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1354. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 27117863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosomal translocation: one step closer to the molecular mechanism.ACS Chem Biol. 2009 Feb 20;4(2):93-107. doi: 10.1021/cb8002946. ACS Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19173642 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The cyclic octapeptide antibiotic argyrin B inhibits translation by trapping EF-G on the ribosome during translocation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 May 10;119(19):e2114214119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2114214119. Epub 2022 May 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35500116 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand and structure-based approaches for the exploration of structure-activity relationships of fusidic acid derivatives as antibacterial agents.Front Chem. 2023 Jan 6;10:1094841. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1094841. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 36688047 Free PMC article.
-
The role of GTP hydrolysis by EF-G in ribosomal translocation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Nov;119(44):e2212502119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2212502119. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36282914 Free PMC article.
-
Reversing the Natural Drug Resistance of Gram-Negative Bacteria to Fusidic Acid via Forming Drug-Phospholipid Complex.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Feb 11;11(2):177. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11020177. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391663 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Activity of Fusidic Acid-Loaded Electrospun Polylactide Fiber Fleeces Against Periodontopathogenic Species.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 24;17(7):821. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070821. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733030 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

