SRSF1 suppresses selection of intron-distal 5' splice site of DOK7 intron 4 to generate functional full-length Dok-7 protein
- PMID: 28874828
- PMCID: PMC5585400
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-11036-z
SRSF1 suppresses selection of intron-distal 5' splice site of DOK7 intron 4 to generate functional full-length Dok-7 protein
Abstract
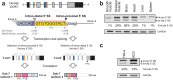
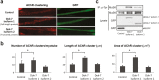
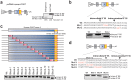
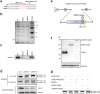
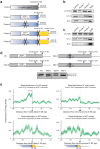
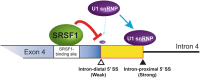
Dok-7 is a non-catalytic adaptor protein that facilitates agrin-induced clustering of acetylcholine receptors (AChR) at the neuromuscular junction. Alternative selection of 5' splice sites (SSs) of DOK7 intron 4 generates canonical and frame-shifted transcripts. We found that the canonical full-length Dok-7 enhanced AChR clustering, whereas the truncated Dok-7 did not. We identified a splicing cis-element close to the 3' end of exon 4 by block-scanning mutagenesis. RNA affinity purification and mass spectrometry revealed that SRSF1 binds to the cis-element. Knocking down of SRSF1 enhanced selection of the intron-distal 5' SS of DOK7 intron 4, whereas MS2-mediated artificial tethering of SRSF1 to the identified cis-element suppressed it. Isolation of an early spliceosomal complex revealed that SRSF1 inhibited association of U1 snRNP to the intron-distal 5' SS, and rather enhanced association of U1 snRNP to the intron-proximal 5' SS, which led to upregulation of the canonical DOK7 transcript. Integrated global analysis of CLIP-seq and RNA-seq also indicated that binding of SRSF1 immediately upstream to two competing 5' SSs suppresses selection of the intron-distal 5' SS in hundreds of human genes. We demonstrate that SRSF1 critically regulates alternative selection of adjacently placed 5' SSs by modulating binding of U1 snRNP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ohno, K. et al. Splicing regulation and dysregulation of cholinergic genes expressed at the neuromuscular junction. Journal of Neurochemistry (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

